Introduction
The application of connectivity in healthcare is of robust importance. It is bringing a paradigm shift in terms of how the sector works, bringing accuracy to the diagnosis and offering on-time and quality treatment. The key factors that enhance the growth include advancements in AI (Artificial Intelligence), rising usage of connected devices, virtual reality and more.
Another key tool used in health systems and hospitals is Remote patient monitoring which offers improved outcomes. It is known to offer healthcare service providers real-time patient vitals, help with medication adjustment, and offer care intervention as per the individual needs, overall enhancing the care quality.
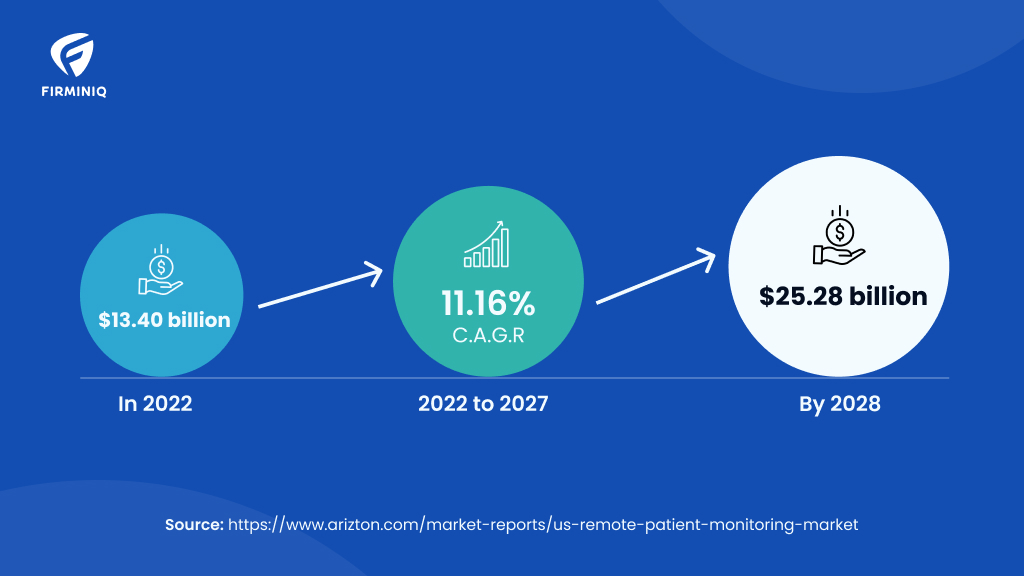
“The US remote patient monitoring market is expected to reach USD 25.28 billion by 2028 from USD 13.40 billion in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 11.16% during the forecast period.”- Arizton
Ever wondered why the adoption rate of RPM varies across countries. The RPM growth is influenced by numerous factors unique to the country’s healthcare landscape. While there is a more developed infrastructure, reimbursement policies, EHR (Electronic Health Records) systems, contributing to the overall growth of RPM. Though India is gradually progressing in digital health, there are numerous factors to be considered to make RPM work. Stakeholders also play a critical role in the successful implementation and functioning of RPM.
The blog explores the factors and stakeholders crucial to making RPM work effectively in the digital health ecosystem
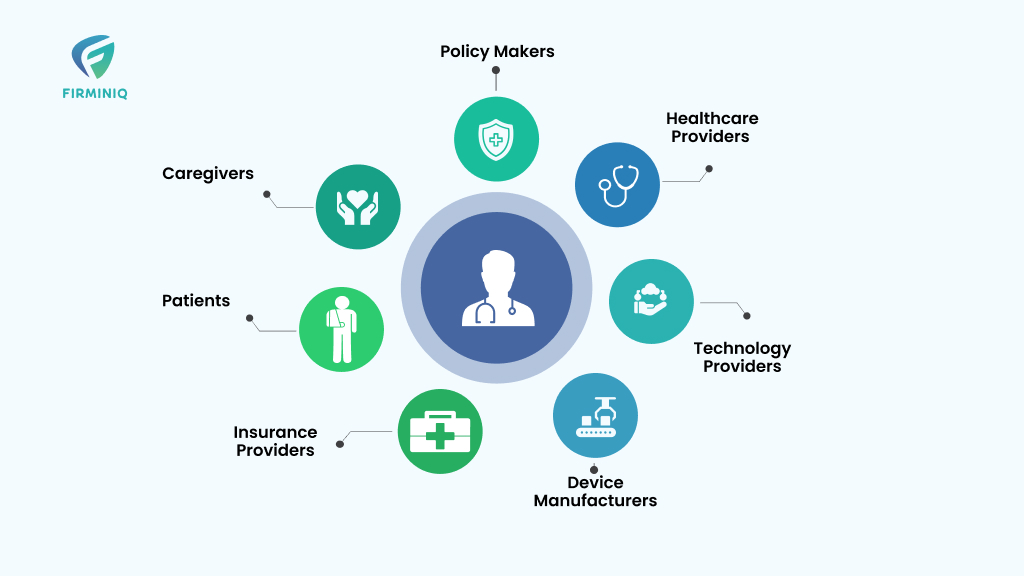
Stakeholders Involved in RPM
1. Healthcare Providers
It includes physicians, nurses, and other care professionals involved. Healthcare providers use RPM by gathering real-time patient data and making effective clinical decisions. It ensures the overall well-being of the patient.
2. Patients
Patients are the active participants availing themselves of the treatment. They use these RPM devices to track their vitals and transmit data to the physicians for further monitoring. RPM allows patients to receive timely interventions and personalized care and more.
3. Caregivers
Caregivers are the ones helping patients with the device setup, data collection offering them care so that they adhere to the monitoring protocols. They may be family members or home healthcare providers.
4. Device Manufacturers
RPM device manufacturers design and build devices that seamlessly enable the monitoring of patients outside of the traditional healthcare model. A few examples of such devices include sensors and wearables that help track patient vitals in real-time and send it to the physician.
5. Technology Providers
These are the organizations providing RPM devices, platforms, and connectivity solutions that are one of the most important stakeholders. From designing user-friendly devices to ensuring data security and seamless data transmission, they are the most responsible stakeholder.
6. Insurance Providers
The insurance providers are the stakeholders who play a key role for the reimbursement and coverage policies. From determining the criteria for eligibility to reimbursement rates, they are responsible for it.
7. Policy Makers
Government agencies, regulatory bodies, and policy makers have a stake in RPM to ensure patient safety, privacy, and regulatory compliance. They develop guidelines, standards, and regulations to govern the implementation and usage of RPM devices and platforms. Regulators and policy makers also influence the reimbursement policies and financial incentives associated with RPM.
Factors that Matter in a Remote Patient Monitoring Environment
To succeed with RPM, several key factors should be considered like security, infrastructure, business models, digital literacy and more. Let us cover them all and understand how these factors impact the working of RPM.
1. Infrastructure and Connectivity
Infrastructure and connectivity in the healthcare centers is the integrated approach that helps enable care in remote locations and allow hospitals to operate in a seamless manner. Here is why it is important in healthcare.
a. For Real-Time Data Communication
Remote patient monitoring relies on the real-time data transmission between the patient’s monitoring devices and the healthcare provider system. It always requires active and robust internet connectivity to ensure seamless and uninterrupted data transfer. Timely intervention reduces complications and eliminates adverse scenarios.
b. For Quick Alerts and Notifications
Also, in RPM alerts and notifications are sent to the patients on a predefined threshold. So, when there is reliable infrastructure and connectivity there are no delays in getting the critical notifications and patient safety remains at the forefront.
c. For Telecommunication and Conferencing
Remote patient monitoring includes audio/video conferencing and teleconsultation between the healthcare provider and the patients. It requires high-quality internet connectivity, to ensure that everything is delivered seamlessly. Without adequate infrastructure and internet, the quality of consultation might get compromised, that further hinders the diagnosis.
d. For Data Security and Privacy
To maintain robust security and privacy, a strong infrastructure and connectivity is necessary. It ensures the appropriate security measures like encryption and authentication protocols are followed and helps protect patient information from unauthorized access and security breaches.
2. Supportive Policies and Reimbursements
Remote patient monitoring policies and reimbursement models for RPM services can drive more adoption. For example, in the US, The American Medical Association has developed specific CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes, that are used for administrative management purposes like claims. Healthcare providers use these codes when billing for RPM services, facilitating appropriate reimbursement.
Also, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services offers coverage for RPM services that fall under Medicare. Such policies promote RPM usage and incentivize care providers and organizations to adopt such solutions. However not every country has such policies and therefore the adoption of RPM in some geographies has become challenging.
3. Skillset
If the healthcare provider has the knowledge, they can leverage the tools, technologies, and software, interpret it in their workflow and ensure the process is seamless. It also allows them to identify trends and patterns for timely intervention of patient data and make informed decisions. Healthcare providers must also adhere to data privacy and security protocols for secure data transmission while ensuring the patient data is kept confidential.
Not only the physicians, but the patients and other stakeholders also must possess the digital literacy to actively participate in their own care via RPM. It allows them to actively use the RPM devices and communicate easily with physicians.
With the right training programs and education initiatives, organizations can ensure that both parties can navigate and utilize remote monitoring devices and platforms efficiently.
4. Affordability and Accessibility
The cost of remote monitoring devices, sensors, and other technologies can pose a challenge. Therefore, prioritizing this ensures that RPM devices are within the reach of patients and healthcare providers.
If the devices are affordable, it facilitates scalability and enables organizations to implement RPM across a wider patient population, without any financial constraint. It allows efficient resource usage, enhances cost savings, and leads to improved patient outcomes.
Government subsidies and financial aid programs in many countries help make RPM devices accessible and affordable. The subsidies directly reduce the patient expenses. However, it is worth noting that these programs require collaboration among the stakeholders –like government bodies, healthcare organizations, tech companies and others address the cost associated with the devices.
5. Interoperability
Without proper healthcare interoperability, data from remote patient monitoring devices, electronic health records, and other systems may remain siloed. This makes data sharing and information exchange challenging tasks. With the fragmented records, healthcare providers may not have a comprehensive detail of the patient information, which hinders the decision-making process.
The difficulty in integrating and reconciling data from various sources disrupts the flow of information and hampers the effectiveness of RPM. To mitigate such challenges, it is necessary for the organizations to invest in robust interoperability services and ensure a seamless data flow.
6. Data Privacy and Security
Lack of security measures leads to unauthorized access to patient data and further data breaches. When sensitive data falls into the wrong hands, it may lead to malicious activities and damage the organization’s reputation.
To maintain the integrity of patient data in the RPM stringent actions taken can restrict access control to third parties. Data protection regulations, encryption, secure data storage, access control are a few aspects that help protect the patient’s information.
Remote Patient Monitoring system must adhere to the privacy regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability) in the USA or GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European region.
7. Collaboration with Stakeholders
Lack of collaboration between different stakeholders involved in the RPM can result in shattered healthcare and delivery. They may not be aligned with their goals and priorities with a lack of understanding, data security risks, and inefficient resource allocation. Without effective care coordination, stakeholders may lack engagement and hinder the implementation and RPM utilization. The healthcare providers may not have access to complete and timely patient information, leading to suboptimal decision-making and care planning.
Collaboration brings together all the expertise from various stakeholders and ensures their collaboration. Every stakeholder contributes insights, knowledge, and inputs leading to overcoming barriers and challenges associated with RPM. This collective perspective helps address concerns and optimize the RPM program design and implementation.
Winding up
RPM implementations have the potential to change the game in healthcare if it is designed well and implemented with the right patients and providers in mind. To make the most out of RPM, working with people, processes and technology is vital. A comprehensive approach to these factors enhances the effectiveness and impact of connected health initiatives in improving patient outcomes and transforming healthcare delivery. Want help with RPM implementation the right way?
Contact FIRMINIQ and understand how we work with the leading healthcare providers and help them solve the challenges faced in RPM implementation.