Leveraging the power of the cloud, healthcare organizations are leading the way to a new era of care, where data sharing plays a key role. The cloud has become synonymous with more connectivity, flexibility, and efficiency required to support the expanding ecosystem, and foster innovation in connected healthcare.
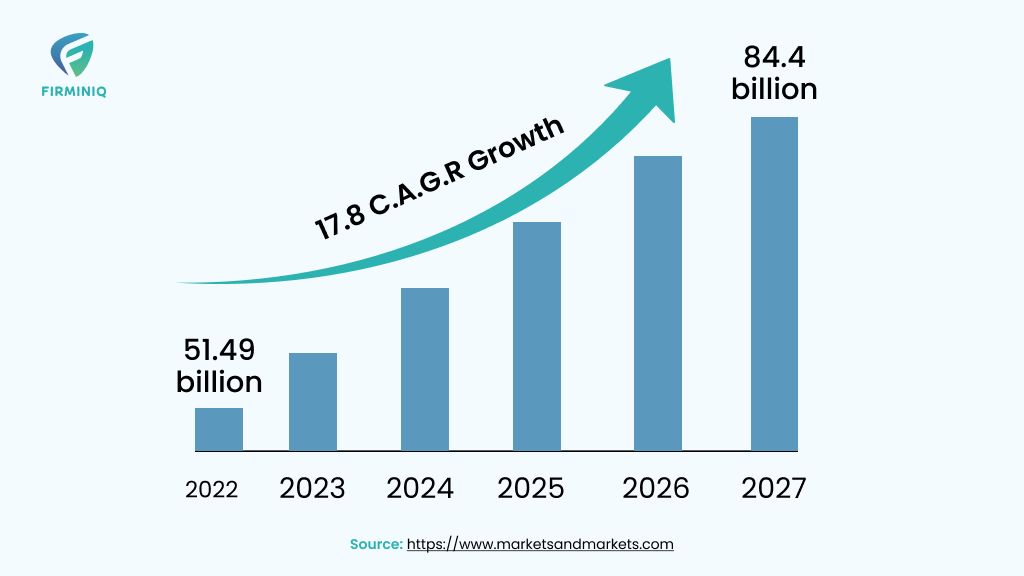
“Global healthcare cloud computing market in terms of revenue was worth $39.4 billion (about $120 per person in the US) in 2022 and poised to reach $89.4 billion by 2027, at a CAGR of 17.8% from 2022 to 2027.”- MarketsandMarkets
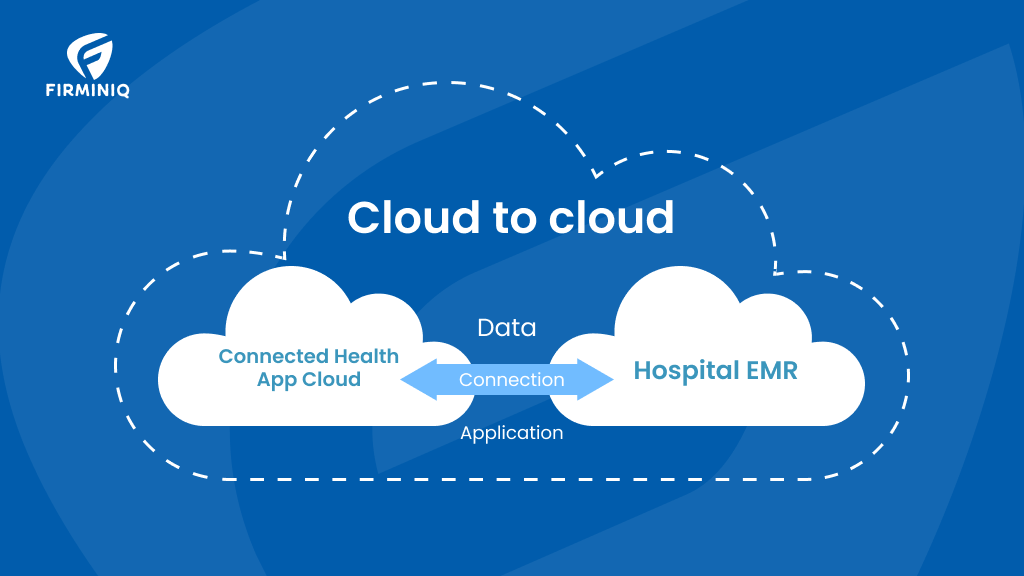
From patient data to medical images, lab results and other administrative documents, providers can upload and store data in cloud storage system. The system offers APIs that allow apps and platforms to exchange data and facilitates integration between EHR (Electronic Health Records) and other systems.
With the cloud-based Health Information Exchange (HIE) platforms, doctors get real-time access, facilitating rapid decision-making and a patient-centric approach.
But there lies the risk of data sharing in healthcare always. From data breaches to other cybersecurity threats, these malicious activities exploit the vulnerabilities in the cloud, potentially compromising sensitive patient information.
As the interoperability increases between the technologies, healthcare organizations must focus on creating a more seamless and integrated technology ecosystem, where the devices and apps can work efficiently. Organizations want to choose the best cloud data sharing services and approaches to solve their scenarios. Here is a blog that shares the benefits of cloud data sharing, the right approach for sharing data, and more. Let us get started!
Significant Impact of Cloud Data Sharing in Healthcare
Adopting the cloud in healthcare technology has brought tons of benefits that lead to enhanced patient care, improved diagnostics, streamlined operations, and more. Know the most significant benefits of cloud data sharing in healthcare:
1. Fosters Collaboration and Connectivity
Cloud data sharing acts as a catalyst for fostering collaboration and connectivity. From offering seamless communication to enabling real-time access to the data cloud empowers stakeholders to work together. The rapid access to data allows professionals to make a precise decision.
2. Interoperability and Integration
As healthcare organizations adopt interoperable solutions, the cloud enables numerous healthcare systems to communicate and share information seamlessly. The patient information is transferred smoothly to different entities. It also reduces manual intervention and allows a large volume of data to be handled easily without errors.
3. Health Information Exchange / Cross Organization Collaboration
The cloud-based health information exchange platforms offer seamless data sharing between different healthcare organizations. Cross-organizational collaboration ensures that clinicians have access to up-to-date patient information that leads to well-coordinated care across healthcare settings.
4. Automates Data Processing
Cloud platforms can impulsively ingest data from sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical devices, and wearables. This ensures that relevant patient information is captured and made available for analysis and decision-making.
5. Enhances Scalability
Healthcare organizations deal with massive amounts of data, including electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, demographics, and more. The scalable infrastructure of the cloud allows the healthcare organizations to handle a large volume of data efficiently while accommodating the growth and changing needs.
6. Easy Access to Analytics
Patient data from various sources is collected and computed in the cloud, therefore with the big data and AI (Artificial Intelligence) algorithms, processing large data sets and extracting valuable insights is made easy.
Analytics on patient data pave the way towards personalized patient care where patient data is used to tailor treatment plans and interventions based on individual characteristics, genetics, and responses to therapies.
Approaches for Healthcare Data Sharing in Cloud
1. Static Data Pattern
The static data pattern is stable where the healthcare data is stored in a cloud repository that remains unchanged over time. The computing and storage here are not entirely independent. That means when the healthcare data is accessed by one service, it may also need to be accessed by another service, data copying is required.
So, briefly, if one copy of the data is modified, it becomes vital to synchronize the changes in other copies.
One of the approach’s potential drawbacks is that it may result in data duplication, meaning multiple copies of the same healthcare data may exist in other services. In Addition, any change in data requires to be replicated across all copies. Deleting data for regulatory requirements needs to be deleted from all the copies. For example, if a patient requests data deletion from one system, it must be ensured that the request is also handled across different systems. Data deletion requests should be executed across all replicated instances to comply with data protection laws. But as the data is copied to multiple systems handling data deletion requests may be challenging and patient data privacy may get compromised.
2. Direct Access No Copy Pattern
In this healthcare data-sharing approach, multiple services within the same cloud environment can access data without moving it. Rather than copying and moving data between services, this pattern allows services to access data directly from the original source. With cloud-native features and technologies, there is seamless data access in real-time and integration across services.
Suppose there is a healthcare network where different hospitals and clinics are connected via cloud-based data-sharing platforms. The platform allows authorized stakeholders to access specific patient data in real time without any duplication. However, it is essential to implement robust security measures and best practices to safeguard patient data adequately.
One of the potential drawbacks of this pattern is that if data is accidentally deleted or compromised, there may be issues with services accessing it, as the data is directly accessed from the source. Any disruption in data availability can cause the services to malfunction and affect the overall performance and availability. Therefore, it becomes vital to keep a backup copy for the data restoration if needed.
3. Multi-Cloud Replication Data Sharing
Also known as the twinning pattern, it is more often used in third party managed systems that allows healthcare organizations to access data from different clouds while enabling seamless access to data for authorized users.
Also, as healthcare data is subject to various regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability) in the United States and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European region, healthcare organizations adopting to multi-cloud replication environments must ensure compliance with relevant data protection and privacy regulations to safeguard patient data and maintain data integrity.
As the pattern allows data to be replicated and shared across multiple cloud environments, there are complexities and risks involved in data security and privacy. Implementing robust security and privacy measures helps us adhere to the relevant regulations.
For example, suppose there is an AI/ML organization that accesses and copies the data from the hospital EMR (Electronic Medical Records) system to their own system. If a patient requests data deletion from the hospital’s EMR system, the hospital should promptly process the request and ensure that the data is removed from their system. At the same time, AI/ML company should also receive the same request, deleting the patient’s data from their system to comply with the regulatory requirements.
4. Multi-Cloud No Copy Data Sharing
It is an approach where the data in healthcare is shared across multiple cloud environments without physically duplicating content or copying it multiple times. The authorized users get access to the data from the source in the different cloud provider’s infrastructures.
For example, different centers are involved in multicenter medical research collaboration. So, every center can seamlessly maintain its own cloud infrastructure and data. There is no need to copy data to other locations with this approach. The researchers can access and analyze data from different centers via virtualization technology from the source without duplicating it.
As data replication and copying is not required in this approach, it offers the advantages of more security and patient data privacy.
Which Cloud-Sharing Data Pattern is Right for Your Healthcare Organization?
Security and data privacy have always been a concern in the healthcare industry data sharing. We have already discussed the appropriate approaches to data sharing, but what about the issues with each approach, and how they can be handled? Let us throw some light and help you choose the right approach:
1. When Multi-cloud replication data sharing is used, organizations must ensure that the data deletion requests by the patients are handled efficiently across different systems. Data deletion requests should be executed across all replicated instances to comply with data protection laws. Compliance like GDPR and others allows individuals to request their personal data deletion
2. As data virtualization does not involve copying data in multi-cloud no-copy data sharing, ensuring data privacy remains a challenge. Organizations must carefully manage access control, encrypt data in transit, maintain audits, and more.
3. HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) and other regulations are crucial for healthcare data protection as they fulfill the specific requirements related to privacy, security, and breaches. Robust security measures in healthcare must be implemented robust security measures to avoid data breaches or unauthorized access. Also, data sharing in healthcare requires a comprehensive approach like legal agreements, privacy assessments, security protocols, and compliance with regulations.
Epilogue
In healthcare, data sharing is one of the most critical aspects and plays a key role in improving patient care, research, and health initiatives. While data sharing in healthcare provides significant benefits, it must be carried out responsibly and ethically, ensuring patient privacy and data security.
The risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks in a cloud environment arises from the shared infrastructure and the potential failure of isolation mechanisms.
Therefore, healthcare organizations must carefully assess their cloud service provider’s security measures, certifications, and compliance with industry standards and regulations. If you are looking for more information on secure data sharing in cloud, reach out to FIRMINIQ.
Do let us know if the blog helped you and if you have any suggestions, do leave us a comment