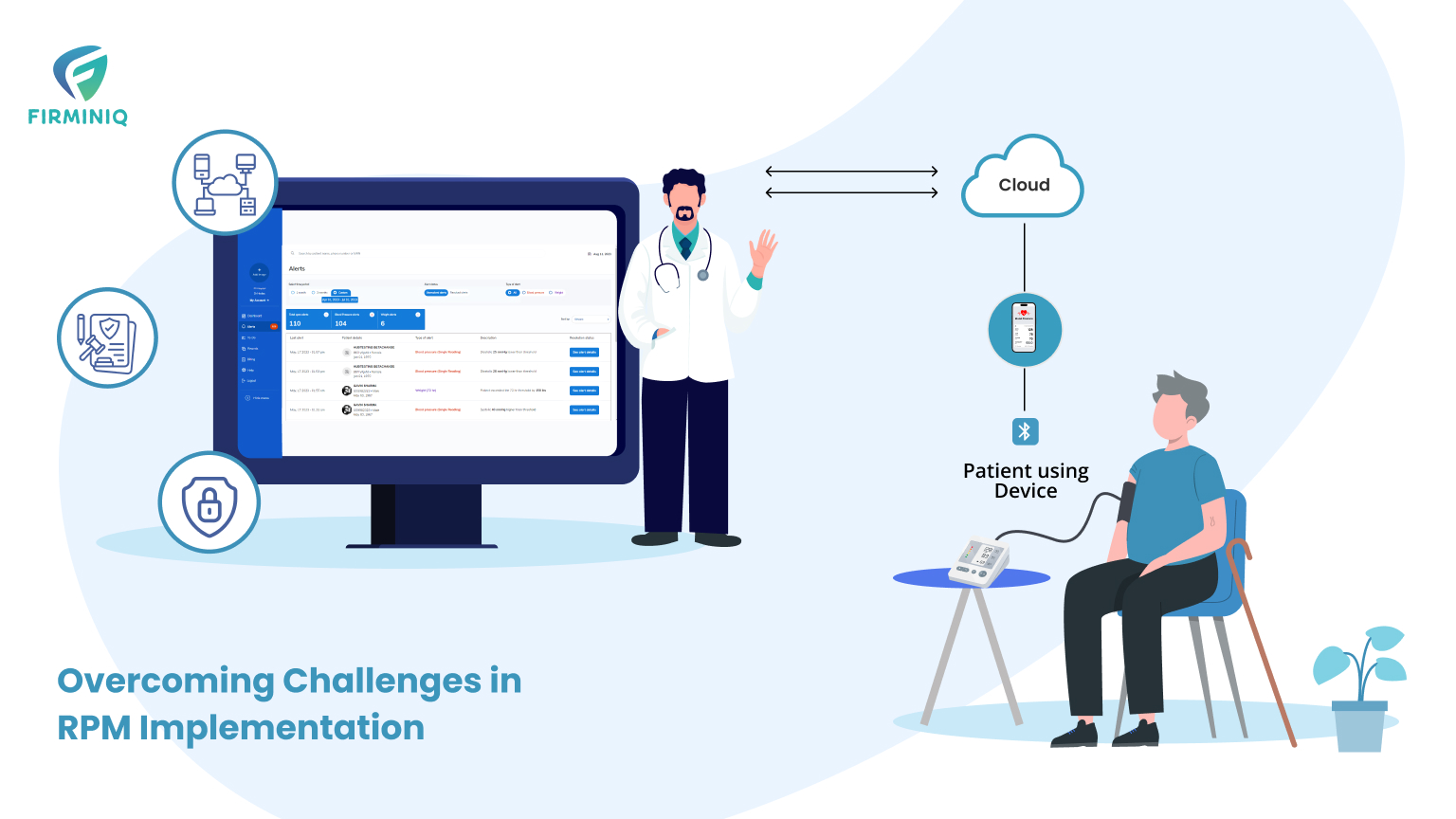
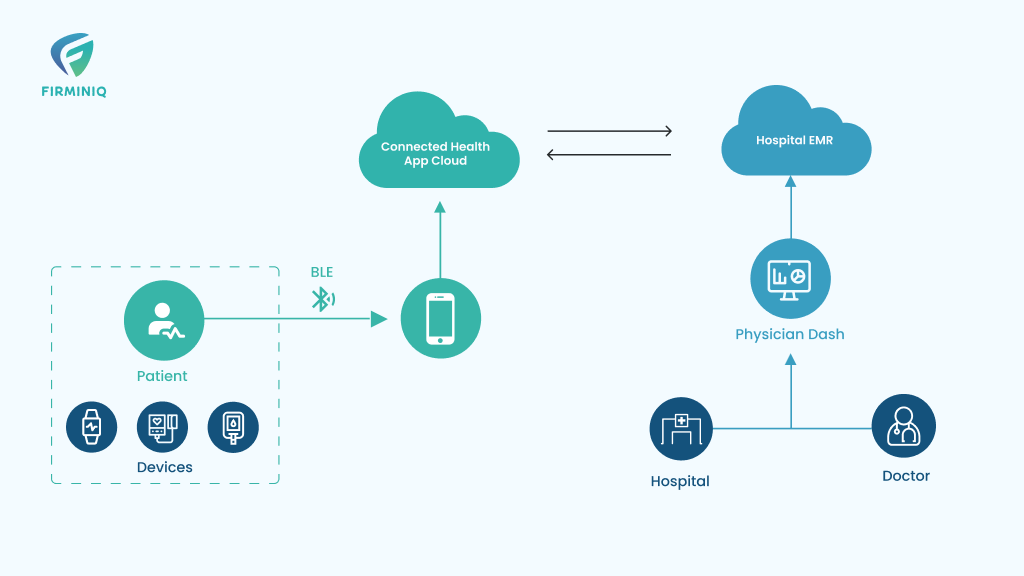
RPM implementation has become a cornerstone for success in modern healthcare that offers a robust approach to patient care. As technology advances, its execution becomes more essential for the providers to deliver efficient care and services. Amid its vast potential to enhance patient outcomes and streamline decision-making, its successful adoption and integration can be demanding.
While RPM has gained significant traction in recent years, organizations face challenges in its implementation. From navigating the compliance guidelines to ensuring seamless communication, and safeguarding patient information, healthcare organizations face many challenges.
Every obstacle requires innovative solutions, and strategic approach organizations must follow to ensure RPM is implemented seamlessly. From technological integration to ensuring meeting regulatory requirements, the journey towards RPM implementation in healthcare requires a holistic understanding of interconnected factors that shape healthcare delivery.
As we navigate through the landscape, it becomes vital for organizations to carefully move through the terrain and escape the challenges that can hamper RPM implementation. Let us explore the obstacles healthcare organizations face and the workable solutions that can help navigate these challenges.
Key Challenges in Implementing RPM Solutions
Let us explore the most notable challenges that organizations encounter during the implementation of RPM.
1. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring regulatory compliance is a key challenge in RPM. The regulation varies across different areas and regions, which makes it challenging for healthcare organizations to implement it accordingly.
For example, in the United States, healthcare organizations should comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and in the European region, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is followed. Navigating these regulations and ensuring compliance can be difficult for the organizations to ensure the implementation of RPM.
2. Safeguarding Sensitive Patient Data
Healthcare organizations transmit and store sensitive patient information like vitals, medical history, personal details, reports, and treatment plans. Unauthorized access by a third party can lead to thefts that can harm the patient.
“One of the healthcare providers experienced a significant data breach impacting 8.9 million individuals, including personal and protected health information, with a ransom demand of $10 million.”- ScienceDirect
Protecting the information from breaches, unauthorized access, and data misuse is vital for the vendors to ensure the data is protected and is not compromised.
Not only this, the unauthorized access to patient-sensitive healthcare information breaches the ethical guidelines and encourages patients to lose their interest and trust in the organization while damaging their reputation.
3. Technology Integration and Compatibility
It is another yet crucial challenge in the implementation of RPM. Effectively incorporating RPM with existing healthcare infrastructure, current workflow and other platforms can be daunting for the organizations. Healthcare professionals are used to their routine and procedure, so it becomes difficult for the organizations to ensure any modern technology integration into the workflow minimizes the disruptions.
Suppose a healthcare organization is using outdated stacks, in that scenario outdated systems may lack the necessary compatibility with modern RPM platforms, leading to hurdles in the integration process. All systems must be compatible to guarantee the accuracy and security of transmitted data.
It hampers the data exchange process between the systems and reduces the efficiency of RPM. Healthcare organizations may also face challenges with integrating RPM with EHR, and clinical systems, which can lead to inefficient data sharing while affecting patient care delivery. Also, RPM implementation requires interoperability protocols to be followed to ensure seamless data exchange, which is another challenge.
4. Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is the biggest challenge healthcare organizations encounter during the RPM implementation. While the RPM offers more convenience to the doctors and patients like improved outcomes and enhanced care delivery, the financial implications are always there against the benefits.
From investing in the upfront cost like hardware, software, and infrastructure to licensing cost, technical staff training there are many cost expenses related to the RPM implementation. Additionally, there may be expenses associated with ensuring regulatory compliance and data security measures.
5. Data Precision and Accuracy
Data accuracy is another challenge that must be addressed carefully. RPM transmits patient data in real-time via devices like wearables. If the data is inaccurate, it can lead to wrong analysis by the physician, and treatment decisions may get compromised.
Calibration of devices, signal interference, device quality, and network issues are a few of the factors that can affect data accuracy.
6. Lack of Patient Engagement
Patient engagement in RPM is vital for their success. However, some patients step back due to fear of switching from traditional to modern healthcare practices and technology usage. The patients may be used to receiving care via in-person visits to the hospitals and are comfortable with that. Using the devices, monitoring the vitals, and communicating with the physician via digital mode may be challenging tasks for the patients.
How to Overcome the Challenges of RPM’s Successful Implementation
1. Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare organizations must focus on developing a framework that addresses compliance requirements like HIPAA, GDPR, FTC (Federal Trade Commission), FDA regulations, and more. From regulatory compliance to outlining clear policies and protocols, organizations should seamlessly handle the patient’s data as per regulatory compliance. Regular audits and assessments can help monitor if the organizations adhere to the regulations.
Also, organizations should focus on conducting regular staff training to ensure the team members are aware of their responsibilities in maintaining regulatory compliance. Regularly updating the training material with new guidelines keeps the staff informed and facilitates better outcomes.
2. Data Protection and Security Measures
Use encryption techniques and ensure other robust security measures to secure and protect data during its transmission and storage. Also, restricted, or limited access control to patient data ensures the data remains secure and only authorized people can access it. Access control mechanisms include using usernames with strong passwords, biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication, and others to verify if the user is genuine.
Organizations can also go for role-based access control (RBAC) that ensures granting access to the personnel with the job responsibility. Assigning roles as per the responsibility like for clinicians, administrators, and other support staff ensures that only authorized persons can access it.
3. Technology Integration
To address the challenge of technology integration in RPM, robust and strategic approaches must be implemented that ensure more efficiency. Assessing the current infrastructure (including hardware and software) helps identify the compatibility issues that arise with RPM implementation. RPM must be compatible with the existing system and recognize any potential challenge for its integration, if any.
Interoperability is another aspect to be considered for technology integration. Ensure to follow the interoperability standards and protocols to ensure seamless communication and data exchange between the RPM system and other healthcare platforms like EHR (Electronic Health Records). Also adopting standards like HL7 (Health Level Seven), and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) helps ensure interoperability between different systems.
4. Strategic Cost-Benefit Analysis
To address the challenge of higher costs, organizations must adopt a strategic analysis plan that helps minimize expenses. A thorough analysis of upfront costs and compliance measures will give a clear understanding of financial implications and help with efficient budgeting.
Estimate the returns on the implementation of RPM and analyze the potential cost and savings. Factors like reduced hospital admissions, readmissions, emergency visits, improved efficiency for chronic management are the greatest potential for cost savings.
5. Data Accuracy
As discussed above, sensors and wearable devices play a significant role in ensuring data accuracy. Therefore, it becomes vital for organizations to use quality sensors and wearables. Ensure to choose the devices that are rigorously tested and validated so that they display accurate readings and other health parameters. Evaluating the performance of the device beforehand helps ensure accuracy in the readings for RPM devices. Calibrating the devices regularly prevents errors as per the industry standards. Quality assurance can help verify the accuracy of the readings before the data is transmitted. Ensuring sensor accuracy is vital to eliminate any hazard linked to inaccurate readings.
6. Patient Engagement
There are always chances of lower patient engagement with the technology. Comprehensive education and training programs for the patients about the usage of RPM, technologies associated with it, devices, and procedures to measure vitals are necessary. User-friendly interface makes it easier for the users to stay connected to the platform.
Conducting sessions and tutorials to help patients or users understand about the monitoring devices, data interpretations, and how to seamlessly communicate with the physician makes it much easier for them to use the platform effectively.
Addressing Key Challenges in RPM Implementation
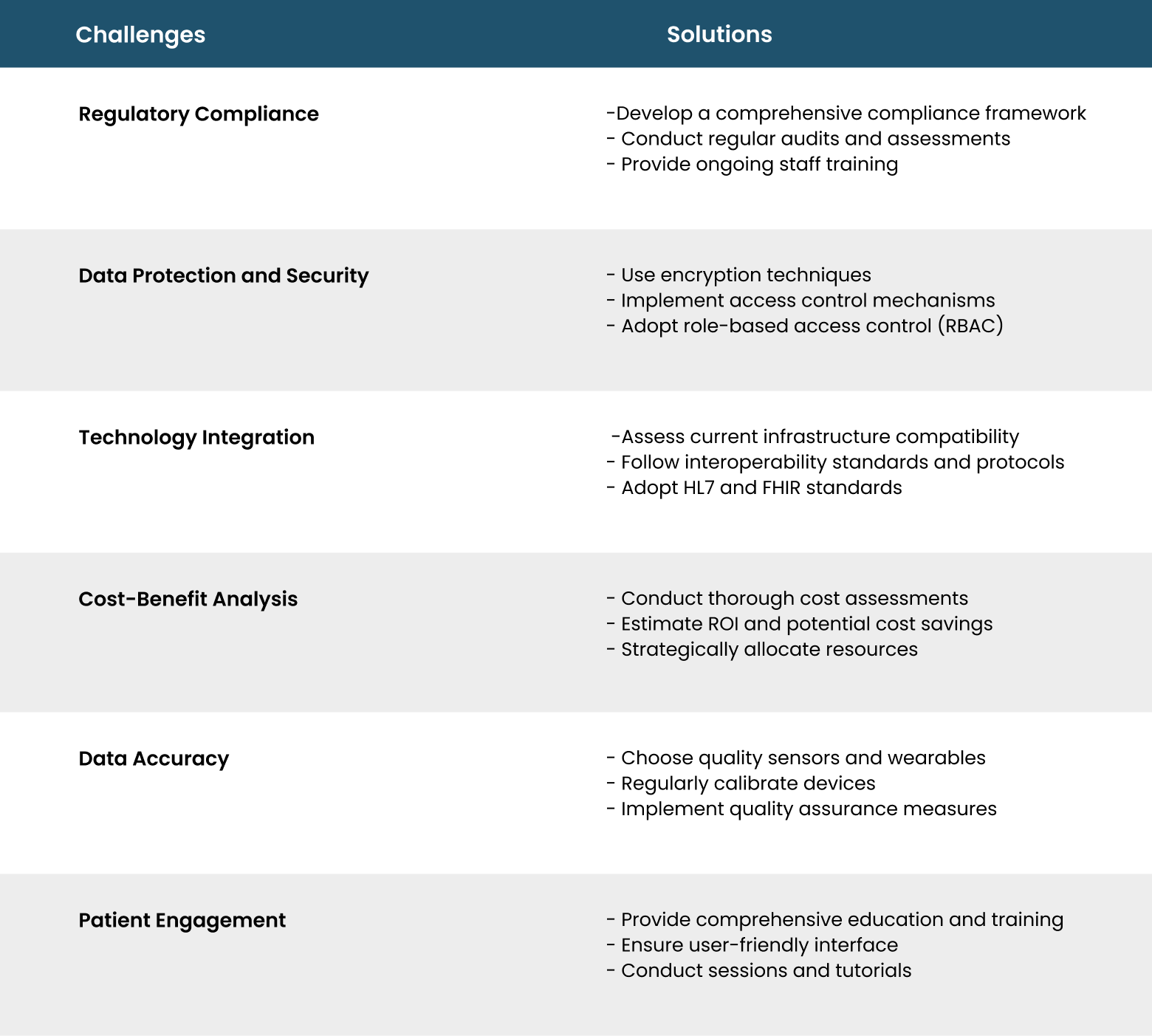
Epilogue
RPM has proved to be a blessing for healthcare, it addresses the needs of different stakeholders including patients and physicians. Patients can leverage RPM and healthcare services in the comfort of their homes, while physicians can track the patient’s vitals and intervene when necessary.
Though there are challenges associated with implementing RPM in healthcare, with the right steps, the problems can be addressed. If you are looking forward to building an RPM solution, we can help you build it as per your specific needs. With robust experience in the domain, we ensure proficient solutions that address the challenges associated with implementing RPM in healthcare. Contact us today to learn more.