What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process that validates an individual’s identity using unique physical or behavioral characteristics. Instead of relying on conventional methods like passwords or smart cards, biometric authentication utilizes biological or behavioral attributes that are challenging to replicate. Common biometric identifiers include:
- Fingerprint Recognition: Analyzing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on an individual’s fingertips.
- Facial Recognition: Using distinctive features of a person’s face, such as the arrangement of eyes, nose, and mouth, for identification.
- Iris or Retina Scanning: Analyzing the unique patterns in the iris or retina of the eye.
- Voice Recognition: Identifying individuals based on their vocal characteristics, including pitch, tone, and speech patterns.
- Hand Geometry: Analyzing the physical structure of the hand, including the size and shape of the palm and fingers.
Phases of Biometric System
We have two phases in Biometric system:
Enrolment Phase
In this phase, the biometric information of the user is recorded in the system database.
Recognition Phase
This is the second phase of the system where the user is authenticated to the system using his biometrics.
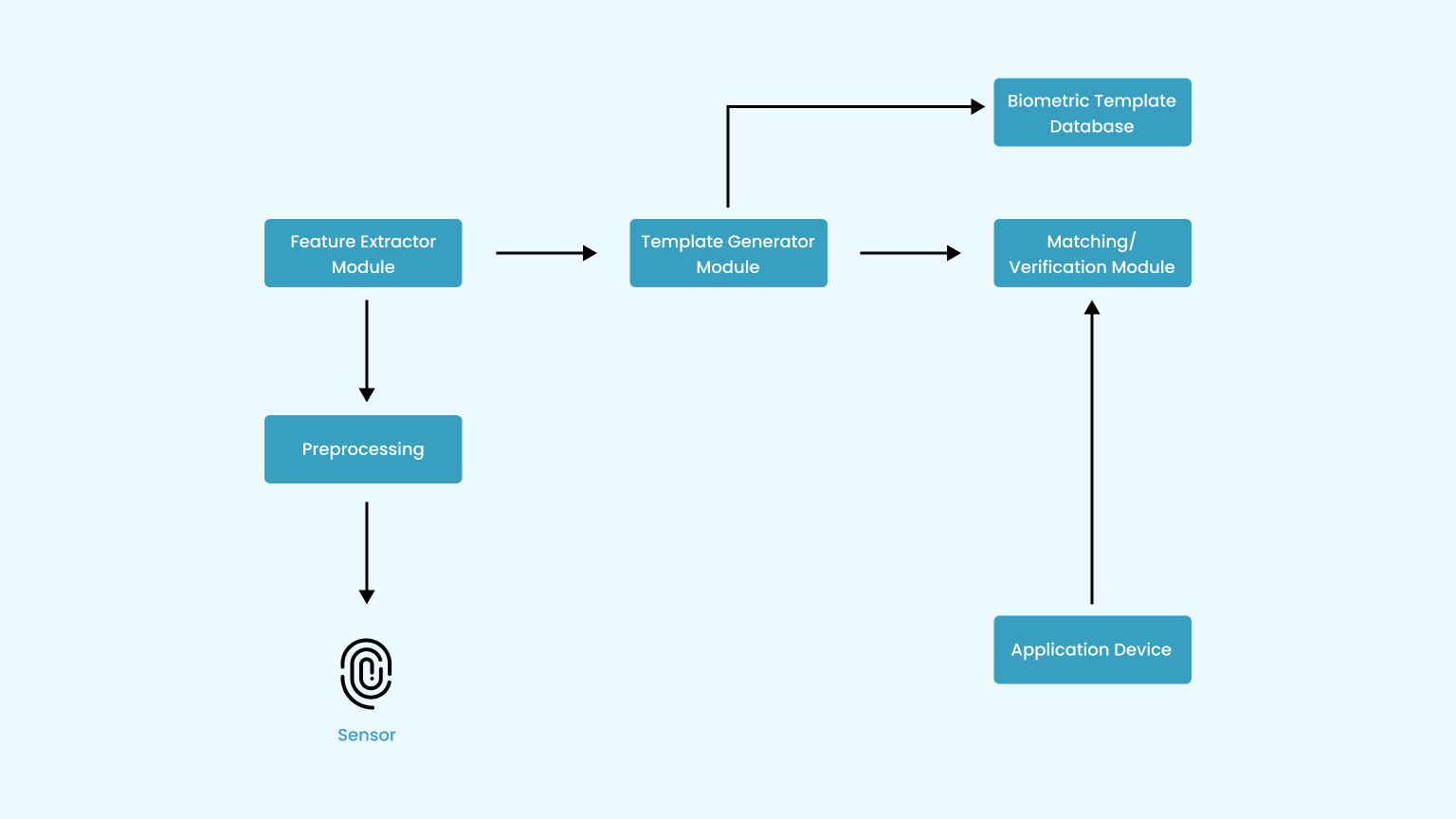
Biometric System Architecture
Sensor
This captures biometric traits from individuals. Fingerprint scanners, facial recognition cameras, iris scanners are some of the commonly used examples.
Preprocessing
Its function is to enhance the input and to eliminate artifacts from the sensor, background noise, etc. It performs some kind of normalization.
Feature Extractor Module
The core function of the feature extractor is to extract relevant and distinctive features from the pre-processed data. These features should be discriminative, meaning they capture the unique characteristics of the individual’s biometric trait.
Template Generator Module
The template generator takes the pre-processed and standardized features and organizes them into a compact and structured format. This format is designed to represent the essential characteristics of the biometric trait while minimizing the storage requirements.
Biometric Template Database
Stores templates derived from enrolled individuals’ biometric data. Should be securely encrypted, and access controls should be in place to prevent unauthorized access. Biometric templates should be anonymized and irreversible to protect individual privacy.
Matching/Verification Module
The matching algorithm compares the features of the presented biometric sample with the features extracted or represented in the stored template. The algorithm computes a similarity or dissimilarity score based on the degree of match between the presented sample and the stored template.
Data Protection
The communication between each module should be properly protected. All the modules can be included inside a common VPC and restrict the communication between the modules within the same VPC. Utilizes secure protocols such as HTTPS to protect data during transmission. This is vital for protecting biometric data during transmission between sensors, feature extraction modules, and databases.
Pros of Biometric Authentication in Healthcare
1. Secure Access to Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Biometric authentication provides a robust method for healthcare professionals to access electronic health records securely. Fingerprint, iris, or facial recognition can be used to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive patient information.
2. Reduction of Identity Theft and Fraud
Biometric methods help in reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud by ensuring that only authorized individuals, such as healthcare providers and staff, can access patient records and perform medical procedures.
3. Patient Identification and Matching
Biometrics can be employed to accurately identify patients, reducing the chances of medical errors associated with misidentification. This is crucial for ensuring that patients receive the correct treatments and medications.
4. Quick and Convenient
Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, provide a quick and convenient way for users to access their devices or systems. The speed of biometric authentication is often faster than traditional methods like entering passwords or PINs. Users appreciate quick and seamless authentication processes. Biometric authentication enhances the overall user experience by reducing the time and effort required to gain access to devices, systems, or physical spaces. Since biometric authentication relies on unique physiological or behavioral traits, users don’t have to remember passwords, reducing the chances of forgetting or resetting them. This can save time and resources for both users and system administrators.
5. Enhanced Access Control in Healthcare Facilities
Biometric access control systems can be implemented in various areas of healthcare facilities, including restricted zones, laboratories, and pharmacies. This helps in controlling access to sensitive areas and substances, ensuring a higher level of security.
6. Time and Attendance Tracking
Biometric authentication can be used to track the attendance of healthcare staff accurately. This ensures that the right personnel are present during critical times and helps in managing workforce scheduling efficiently.
7. Patient Privacy and Consent
Biometric authentication can be integrated into systems that require patient consent, ensuring that only the patient or authorized representatives can provide consent for medical procedures or data sharing.
8. Emergency Situations
We need to get the patient records as quickly as possible, in emergency situations. Biometric authentication methods can facilitate rapid access to critical patient information, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions promptly.
Cons of Biometric Authentication in Healthcare
While biometric authentication offers numerous benefits, it is important to address privacy concerns and implement robust security measures to protect biometric data from unauthorized access or misuse. Also, organizations should stay informed about evolving technologies and best practices in biometric security.
1. Privacy Concerns
Biometric data is highly sensitive and personal. In healthcare, where patient confidentiality is paramount, the collection and storage of biometric information raises significant privacy concerns. Unauthorized access or breaches could lead to severe consequences for individuals.
2. Data Security Risks
Storing biometric data requires robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and potential breaches. If a healthcare organization’s systems are compromised, the biometric data of patients could be at risk, leading to identity theft or other malicious activities.
3. Accuracy and False Positives/Negatives
Biometric systems, while advanced and efficient, are not foolproof and may occasionally yield false positives or false negatives. This means there is a chance of incorrect identification or denial of access, potentially leading to issues with patient records or access to critical medical information.
4. System Vulnerabilities
Like any technology, biometric systems are susceptible to hacking or exploitation. If not properly secured, these systems could be vulnerable to cyberattacks, putting patient data and the overall integrity of healthcare systems at risk.
5. Integration Challenges
Integrating biometric authentication systems with existing healthcare infrastructure can be challenging. Compatibility issues with electronic health record (EHR) systems or other healthcare technologies may arise, requiring additional resources and time for implementation.
6. Cost of Implementation
Implementing biometric authentication systems in healthcare settings can be costly. This includes the cost of acquiring and installing the necessary hardware and software, training staff, and maintaining the systems. Small healthcare providers may find it challenging to allocate resources for such implementations.
7. Lack of Standardization
The lack of standardized protocols for biometric data in healthcare can pose challenges. Interoperability issues may arise if different healthcare systems use different biometric authentication methods, making it difficult to share information seamlessly.
8. Patient Acceptance
Patients may have concerns about the use of biometric authentication in healthcare, including fears about the security of their biometric data and potential misuse. Resistance from patients can hinder the successful adoption of such systems.
9. Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare organizations need to comply with various regulations and standards regarding the storage and protection of patient data. Meeting these compliance requirements, especially concerning biometric data, can be complex and may require ongoing efforts to stay current with evolving regulations.
How to Secure Biometric Details
Securing patient biometric details requires careful planning, implementation of security best practices, and adherence to relevant regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. Here are key considerations to help ensure the secure storage of patient biometric information:
1. Storage
It is safer to store biometric data in an edge-based storage system. Edge based biometric storage provides privacy, low latency, offline functionality and can simplify compliance with data protection by keeping data closer to its source.
2. Encryption
Encrypting biometric data is crucial for protecting the privacy and security of individuals. When selecting an encryption algorithm for biometric data, it’s important to consider factors such as the level of security required, performance, and compatibility with the specific biometric system in use. Here are some commonly used encryption algorithms for securing biometric data.
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman)
- Homomorphic Encryption
- Biometric Cryptosystems
3. Access Controls
Access controls to a biometric template database are critical for ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive biometric information. Proper access controls help prevent unauthorized access, modification, or disclosure of biometric templates. Implement robust access controls to restrict access to patient biometric details. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to the data.
4. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Require multi-factor authentication for accessing the storage system. This adds an additional layer of security beyond a username and password, enhancing protection against unauthorized access.
5. Secure Communication
Ensure that communication between your healthcare systems and the infrastructure is secure. Use secure channels such as virtual private networks (VPNs) or dedicated private connections to transmit sensitive biometric data, between biometric device and storage.
6. Regular Security Audits and Monitoring
Conduct regular security audits and monitoring of the infrastructure. Implement logging mechanisms to track access to patient biometric data and promptly investigate any suspicious activities or unauthorized access.
7. Data Residency and Compliance
Be mindful of data residency requirements and choose service providers that comply with relevant healthcare data protection regulations, such as HIPAA or other local regulations. Ensure that your provider offers compliance certifications and adheres to industry best practices.
8. Data Backups
Regularly backup patient biometric data and ensure that the backups are also encrypted. Having a robust backup strategy helps in data recovery in the event of data loss, corruption, or other emergencies.
9. Better Hardware Support
Invest in high-quality sensors that capture more detailed and unique biometric data. This can include sensors with higher resolution for fingerprints, advanced cameras for facial recognition, and precise iris scanners.
10. Vendor Security Assessment
If you are using a third-party service provider, conduct a thorough security assessment of the provider’s infrastructure, policies, and practices. Ensure that the vendor complies with security standards and is transparent about their security measures.
11. Data Minimization
Only store the minimum necessary biometric data required for healthcare operations. Avoid storing redundant or excessive information to minimize the impact of a potential data breach.
12. Employee Training and Awareness
Train your staff on security best practices and create awareness about the importance of safeguarding patient biometric information. Human error is a common factor in data breaches, so ensuring that employees are well-informed is crucial.
13. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Understand the legal and ethical considerations related to the storage of biometric data. Obtain informed consent from patients and communicate transparently about how their biometric information will be used and protected.
Conclusion
By implementing these measures, healthcare organizations can enhance the security of patient biometric data and demonstrate a commitment to privacy and compliance with relevant regulations. Regularly reassess and update security measures to adapt to evolving threats and technology advancements.