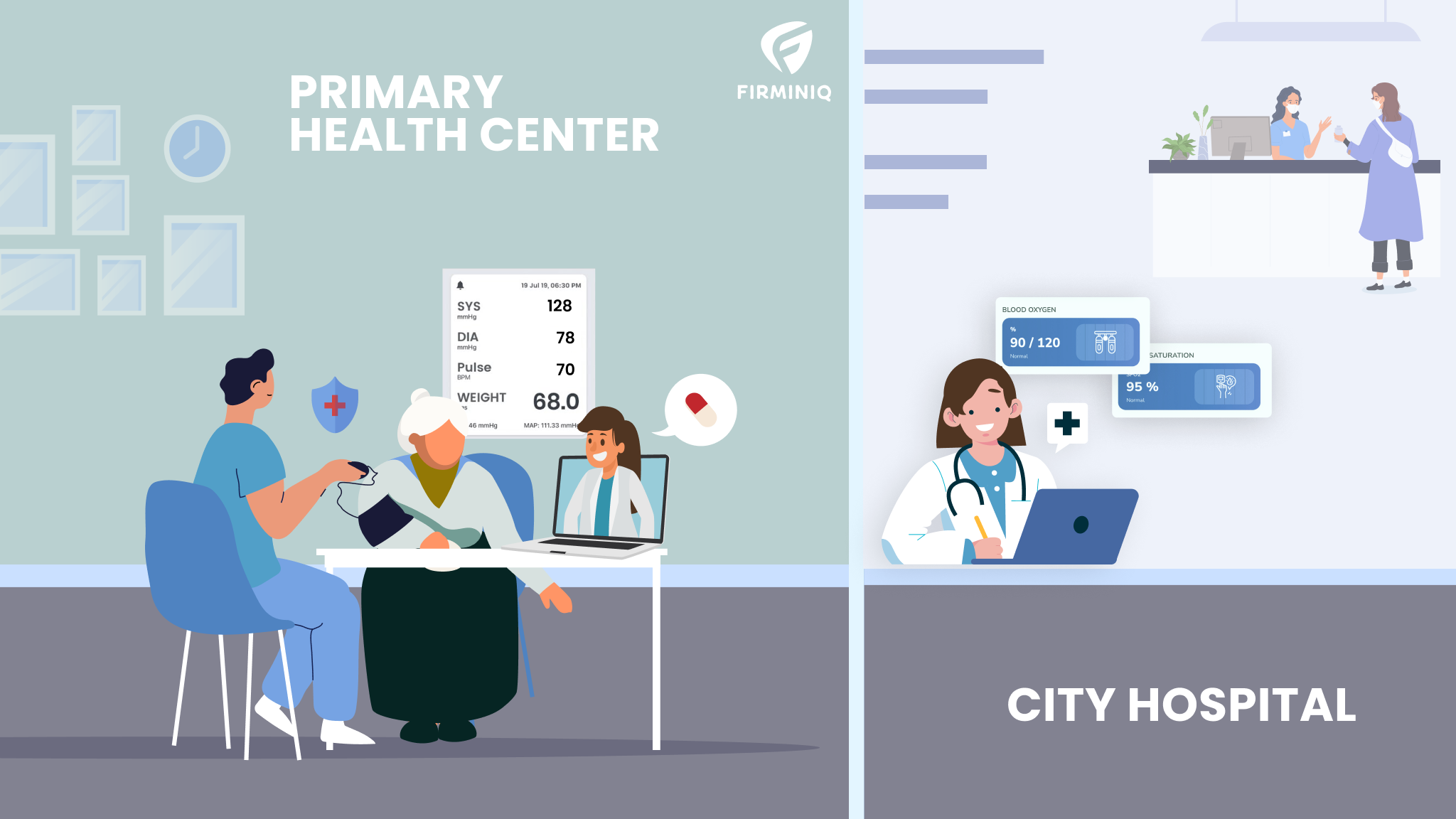
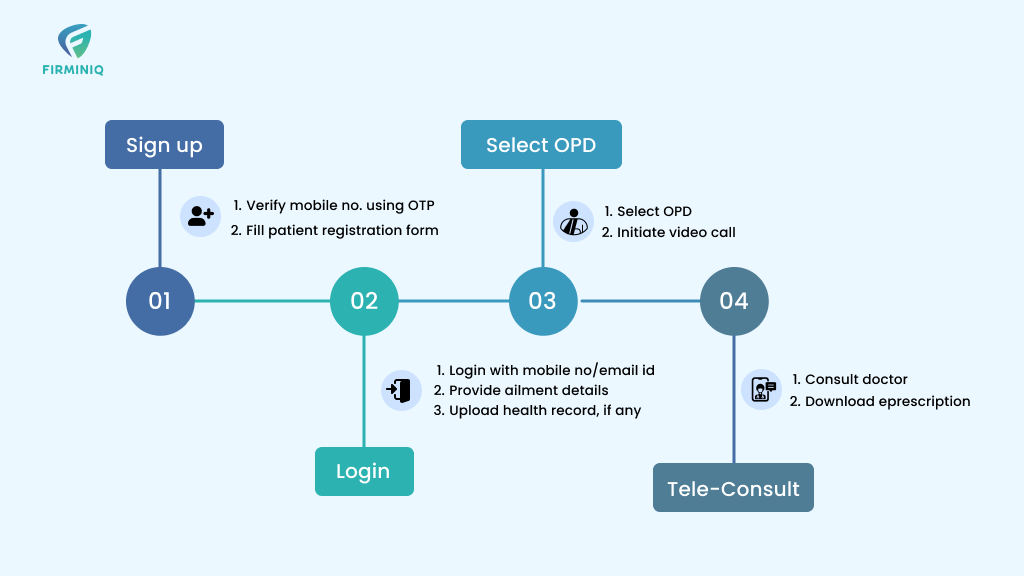
In recent years, telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in the healthcare ecosystem, especially for developing nations. Advanced digital information, communication technology, remote monitoring, and more are the essential components that improve healthcare delivery in developing nations and people living in remote areas.
As per Telehealth and Medicine Today, among “India’s national population of more than 1.35 billion people, 72.2% live in rural areas, while more than 75% of doctors are based in cities.” Also, “An estimated 3.4 billion people – around 45 percent of the global population – live in the rural areas of developing countries. “The statistics depict the need for solutions like RPM and telehealth to bridge the gap and ensure that rural and underserved areas can get access to medical care.
There are many government initiatives that have been adopted by developing countries, helping millions of patients to have access to healthcare without having to physically visit the doctor or hospitals. These initiatives highlight the potential of telehealth to revolutionize healthcare delivery, making it more patient-centered, efficient, and cost-effective. The blog covers the key government healthcare initiatives and what benefits do they offer to stakeholders.
Key Government Telehealth Initiatives
1. India: National Telemedicine Service
To bridge the national health divide India’s ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched an eSanjeevani initiative, a step towards digital health equity to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and offer healthcare services to masses. From offering remote consultation to physicians to patients to facilitating doctor-to-doctor teleconsultations it operates in 2 models. It also allows access to quality healthcare services by visiting Ayushman Bharat Health & Wellness Centre.
The initiative has seen widespread adoption, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, helping millions of patients access healthcare without physically visiting healthcare facilities.
2. Brazil: Telehealth Brazil Networks Program
The development of a telehealth model for primary care in Brazil arose from the necessity to address two major issues including the insufficient number of physicians equipped to handle primary care, and the challenge of placing healthcare professionals in remote areas.
Telehealth Brazil Network Program relies on telehealth resources with the objective of carrying out teleconsultations and permanent education for healthcare professionals. It also focuses on the provision of digital tools to improve healthcare delivery. Integrating the program into the healthcare system allowed Brazil to have quality and access to healthcare services, and reduced wait time, hospitalizations, and more.
3. South Africa: National Department of Health’s Telemedicine Program
According to the National Library of Medicine, South Africa was an early adopter of telemedicine in the late 1990s. Phase one of the National Telemedicine System was launched by the National Department of Health in 1999 at 28 sites in six of the nine provinces
It has developed a telemedicine program to address healthcare disparities in rural areas. This program focuses on teleconsultations, tele-education, and the establishment of telemedicine centers equipped with the necessary technology. The program has improved the quality of care in rural areas, provided specialist consultations to patients who would otherwise have to travel long distances, and supported healthcare workers with training and resources.
4. Kenya: Ministry of Health Telehealth Initiatives
“In the Kenyan case, telemedicine played an instrumental role during the COVID-19 pandemic as patients experienced worse outcomes due to the disruption of medical service.” –Research Gate
The health ministry of Kenya implemented telehealth initiatives that offered patients a platform for the continuation of care. From teleconsultation, remote diagnostics, and mobile app usage, telehealth was a part of addressing the disruptions in healthcare.
Programs like “mHealth Kenya” understand the transformative potential of technology in enhancing healthcare outcomes. The program is dedicated to creating and deploying digital solutions that tackle critical health challenges in Kenya and beyond. The initiative supports disease management, responds effectively to public health emergencies, and provides healthcare workers with the essential tools to deliver high-quality care.
5. Indonesia: SehatQ and Halodoc Platforms
One of the leading healthcare platforms in Indonesia that changed the entire healthcare game. The government has partnered with telehealth platforms like SehatQ and Haldoc. “Halodac connects nearly tens of millions of users with more than 22,000 general practitioners and 1,200+ pharmacies through a single mobile app on Android and IOS platforms.”
The platform offers teleconsultations, pharmacy consultations, health education and more to the patients. Also, via integration of such services, there is an improved access to healthcare in Indonesia, while ensuring that patients could receive timely care and medications.
6. Philippines: National Telehealth Service Program (NTSP)
As per National Telehealth Center “NTSP facilitates consults between primary care physicians in geographically isolated and disadvantaged areas (GIDA) and clinical specialists of the Philippine General Hospital (PGH) using a mobile and internet-based interface and triaging system.”
The program focuses on improving healthcare access in remote and underserved regions. It covers teleconsultations, teleradiology, and telepathology services. By leveraging technology, NTSP aims to reduce healthcare disparities and enhance the quality of care across the country.
Benefits of these Government led Initiatives
Government-led initiatives offer many benefits for the patients and healthcare providers. Let us focus on some of the key benefits:
1. Enhances Access to Healthcare
Telehealth and RPM help bridge the gap between urban and rural healthcare services, while ensuring that patients living in remote areas have access to quality care, without having to travel. Telehealth platforms, such as video consultations, phone calls, and mobile health applications, allow patients to connect with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes. Patients can receive consultations from specialists who may not be available locally, enhancing the quality and comprehensiveness of care.
2. Reduced Costs
Patients save on travel costs and time by receiving care remotely. Leveraging RPM is particularly beneficial for those living in remote areas who would otherwise have to spend considerable money and time traveling to urban centers for medical care.
3. Improved Care Quality
Telehealth, remote monitoring and government initiatives allow patients to get rid of waiting in long queues to consult their physicians. Via chat or call support, they can consult the physician anytime, leading to a quick diagnosis and treatment plan. It is quite beneficial for patients with chronic conditions and requires immediate attention.
4. Timely Interventions
As RPM helps detect the symptoms at an early stage, physicians can intervene before the condition gets worse, especially in the case of chronic illness. Patients dealing with diabetes, hypertension, and other heart-related issues can be seamlessly addressed with the initiatives. Also, in case of emergencies, telehealth platforms ensure seamless communication between doctors and physicians, so that patients receive timely care.
5. Convenience for Patients
The government initiative allows patients to consult physicians from the comfort of their homes, saving plenty of time and money. It is beneficial for patients and allows physicians to save resources and manage their time more efficiently. Also, telehealth offers flexibility for the patients so that they can book the appointments as per their availability, which reduces the likelihood of missed appointments.
Epilogue
The government-led initiatives have marked a new era of healthcare delivery for developing countries while making it easier for the stakeholders to invest in solutions like RPM. Leveraging advanced technologies, and ensuring seamless communication is making it easier to address critical health challenges and ensure quality medical care is accessible to all.
Healthcare organizations must prioritize patients’ needs and ensure that healthcare services are safe, secure, and accessible. Wish to leverage the power of remote patient monitoring and ensure patients’ needs are met? Reach out to us.