Ever wondered about security breaches in healthcare? The primary culprit behind these incidents is often the failure to adhere to compliance standards.
Non-compliance can have profound consequences due to the risk of exposing sensitive patient information. The breach of regulatory standards jeopardizes the privacy and security of individuals and opens the door to legal consequences and reputational damage for the entities involved. The 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report reveals that the healthcare sector incurred the highest average cost for a data breach, standing at $10.93 million, surpassing all other industries.
Therefore, regulatory compliance becomes imperative in ensuring the integrity and success of healthcare-related endeavors. Regulatory compliance takes center stage and ensuring that the healthcare apps adhere to the emerging rules and regulations is pivotal to define success. Compliance not only minimizes the risk of data breaches but also plays a significant role in maintaining the integrity and success of healthcare apps. These regulations are not mere legal requirements; they form the bedrock of responsible and patient-centric healthcare.
The blog helps you discover the top compliance regulations shaping the landscape for healthcare apps.
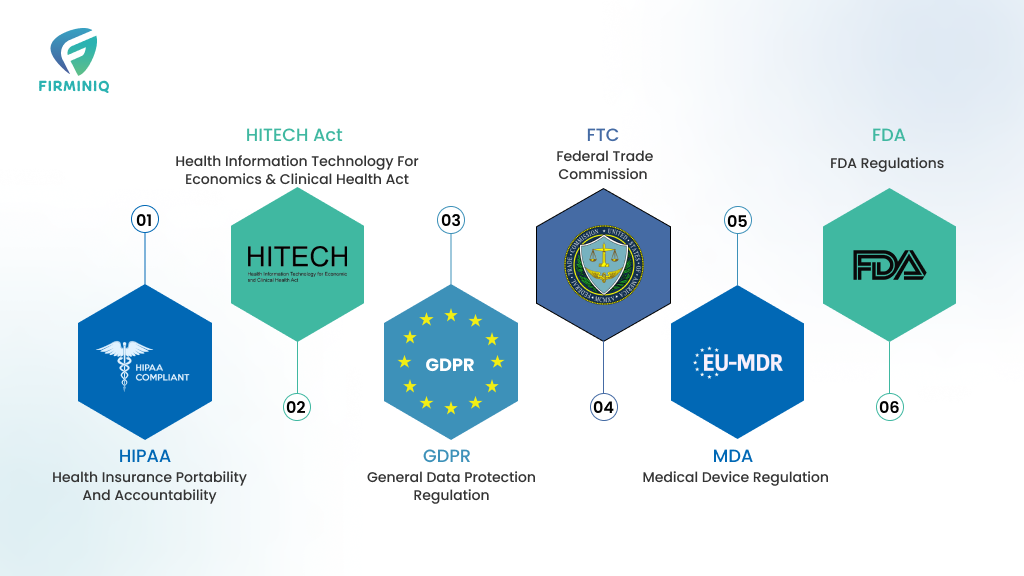
Key Regulatory Compliances for Healthcare App Development
Health apps enable the sharing of sensitive information. Therefore, it is vital to remain conscious of compliance requirements and adhere to regulations to effectively safeguard health information. The guidelines ensure that the healthcare apps can operate seamlessly, securely with the legal framework to safeguard patient data and public health.
Let us explore the key regulatory compliances in the healthcare app development:
1. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability)
HIPAA sets a national standard for protecting individual health information in the United States healthcare landscape. It is a regulatory framework that demands strict adherence to established standards. All organizations that deal with PHI (Protected Health Information) must have a secure infrastructure and top-notch security to ensure compliance. Other medical institutions worldwide are embracing the HIPAA framework as the primary security guidelines to adhere to.
The main objective is to safeguard patient privacy and secure healthcare information exchange. Examples of HIPAA compliance includes implementing appropriate security measures while transferring or storing PHI and ensuring third parties can handle information and comply with HIPAA.
2. HITECH Act
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, passed in 2009, is part of the broader American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. Its main goal is to encourage the adoption and meaningful use of health information technology in the United States. HITECH serves as an incentive for the meaningful use of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) while simultaneously reinforcing the privacy and security provisions outlined in HIPAA.
For healthcare apps operating in the United States, understanding, and complying with the HITECH Act involves taking concrete steps to protect electronic health information, promptly notifying relevant parties in case of a breach, and utilizing technology in ways that meaningfully contribute to improved healthcare outcomes.
One example is, HITECH introduced regulations concerning data breach notifications, a concept echoed and expanded upon by HIPAA’s Omnibus update. This update not only reinforced the data breach notification rules but also specified that healthcare providers’ business associates would be held equally accountable for data breaches, sharing the same liability as the providers themselves.
3. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
For healthcare applications serving in the European Union, complying with the General Data Protection Regulation is necessary. It is a comprehensive set of practices with key components including explicit user consent, transparent data processing practices, and data security measures and allowing users control over their data.
Aligning to the GDPR requirements allows healthcare apps operating in the European region to demonstrate a commitment to ethical data practices and protect individual privacy rights.
4. Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
In competitive healthcare markets, consumers enjoy reduced costs, improved care, and increased innovation. The Federal Trade Commission plays a crucial role in upholding antitrust laws within healthcare markets to prevent any anticompetitive practices that could negatively impact consumers.
It offers essential support and guidance for healthcare app developers and providers to ensure compliance with U.S. antitrust laws. The agency also provides various participants in the healthcare market, including physicians, health professionals, hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, sellers of healthcare products, and insurers, to assist them in adhering to U.S. antitrust laws. In the dynamic landscape of healthcare apps, where innovation is key, the FTC actively monitors mergers and acquisitions within the healthcare sector.
5. Medical Device Regulation
Implementation of Medical Device Regulation (MDR) within the European Economic Community (EEC) has profound implications for the development and integration of medical devices in the digital space.
MDR, effective for EEC, involves oversight and control of medical devices to ensure their safety, efficiency, and quality. MDR replaced MDD (Medical Device Directive) and brought about significant improvements for healthcare app developers and providers.
For app developers, navigating the regulatory landscape was challenging due to the opacity of the legislation and the associated hurdles. MDR addresses these issues by offering a more streamlined and transparent regulatory framework. The legislation has become opaque, creating challenges and delays for manufacturers seeking to introduce new products to the market. Additionally, the regulation of medical devices posed difficulties. But MDR led to an improved transparency, reduced time from innovation to market, and a better overview of available medical devices.
6. FDA Regulations
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an integral part of the US Department of Health and Human Services, oversees and governs the development, manufacturing, safety, efficacy, and marketing of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and biologics. The regulation guarantees that any software app or standalone device released to the public is secure and undergoes comprehensive evaluations for potential risks following their established rules and regulations.
Key considerations under FDA regulations include conducting thorough risk assessments, providing evidence of the app’s safety and efficacy, and complying with specific quality system regulations.
Let us delve deeper into specific aspects of FDA regulations that relate to software and home use medical devices.
Class 2 (Moderate to High Risk)
These are complex devices with a moderate level of risk. They are bound to standard controls applicable to Class 1 devices but must also ensure compliance with special controls like performance standards, post-market surveillance, and more.
Examples include some pregnancy test kits, infusion pumps, blood pressure monitors and more.
Class 3 (High Risk)
These devices are subject to both general and special controls, have elevated risk and are often used to sustain a human life. They also need pre-market approvals from the FDA before getting released in the market.
Examples include implantable pacemakers and other life-supporting software applications.
SaMD (Software as a Medical Device)
SaMD may work on general-purpose (non-medical) computing platforms; may be used in combination with other products including medical devices; and may interface with other medical devices or other general-purpose hardware and software that provide input to SaMD.” It can interface with various other medical devices, both hardware and software, as well as general-purpose software.
A few examples of SaMD include diagnostic imaging software that enable smartphones to visualize diagnostic images from MRI devices, health monitoring apps, and medication management software.
Influence of Regulations on the Healthcare Landscape
The landscape of healthcare app development is woven by the combination of regulatory compliance measures that help safeguard patient information while ensuring privacy is central to healthcare, ensuring ethical practices, and sustaining the highest standards of healthcare delivery. The requirement of HIPAA in the USA to GDPR commitment to user data protection in Europe, and vigilant oversight of FDA regulations serves as a committed beacon in healthcare. The regulations ensure emergency medical services are accessible to all patients, no matter what their financial condition is.
While the HITECH Act advocates for the adoption of technology for improved patient care. HL7 (Health Level Seven International) standards and the recognition of SaMD underscore the importance of seamless data exchange and innovative technologies in shaping the future of healthcare.
Stark Law, Anti-Kickback Statute, Federal Trade Commission, CPT, and ICD Coding Standards, Bring Your Own Device are other vital healthcare regulatory compliances that significantly influence the ground for healthcare apps.
How can FIRMINIQ assist you in adhering to healthcare compliance regulations?
In the healthcare sector, engaging with regulatory authorities and meeting all the provisions is a foundational measure towards safeguarding patient data, upholding ethical responsibility, and fostering trust between healthcare practitioners and users. Adhering to standards like HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, HITECH, and others helps maintain the security of patient data on the apps.
As a trusted healthcare software development company, our expertise lies in crafting mobile applications and software solutions that comply with the legal requirements and regulations governing the industry. Our well-informed developers deliver tailored solutions that cater specifically to your requirements, guaranteeing optimal results.