Amidst the swift progress of technology, the healthcare sector is experiencing a transition through the development of healthcare apps. These applications are reshaping how healthcare is accessed, providing convenience and personalized experiences. From monitoring patient conditions in real-time to seamless communication, the convenience offered by these apps empowers patients and enhances engagement.
“The global mHealth apps market size was valued at USD 43.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.6% from 2023 to 2030.”- Grand View Research. This statistic is not merely a numerical representation; it signifies a dynamic shift in the paradigm of healthcare, driven by the advancing trajectory of mobile technology.
This progress is propelled by numerous factors, including technological innovations, increased adoption of wearables, and a growing emphasis on proactive healthcare management. This trend towards technology implies a future in which mobile applications play a pivotal role in transforming the delivery and experience of healthcare services.
Beyond Convenience: Paradigm Shift in Healthcare
The impact of healthcare mobile applications extends beyond convenience, while becoming a cornerstone in patient-centric and data-driven healthcare. From real-time monitoring of vital signs to proactive health management, healthcare applications are becoming an integral part of the digital revolution. Let us further delve into how this proactive approach replaces the traditional healthcare model, while placing individuals at the forefront of their healthcare journey.
The Factors that Drive Advancement of Healthcare Mobile Applications
The advancement of healthcare mobile applications is propelled by factors such as technological innovations including AI (Artificial Intelligence), Blockchain, IoT (Internet of Things), and more. Let us delve deeper into these elements:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
With integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the healthcare applications extensive medical data can be analyzed to identify patterns, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
For example, wearable devices can gather information on a patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and additional vital signs. Subsequently, AI and ML algorithms can analyze this data to pinpoint potential health risks.
AI algorithms enable the development of personalized and more effective treatment plans. By leveraging data, healthcare providers can make faster and more informed decisions, resulting in improved patient outcomes.
It also empowers healthcare providers to create a personalized treatment plan that can be tailored to the patient’s history, genetics, and lifestyle. AI-powered chatbots enable healthcare providers to engage with patients, offering personalized recommendations and guidance for managing their health.
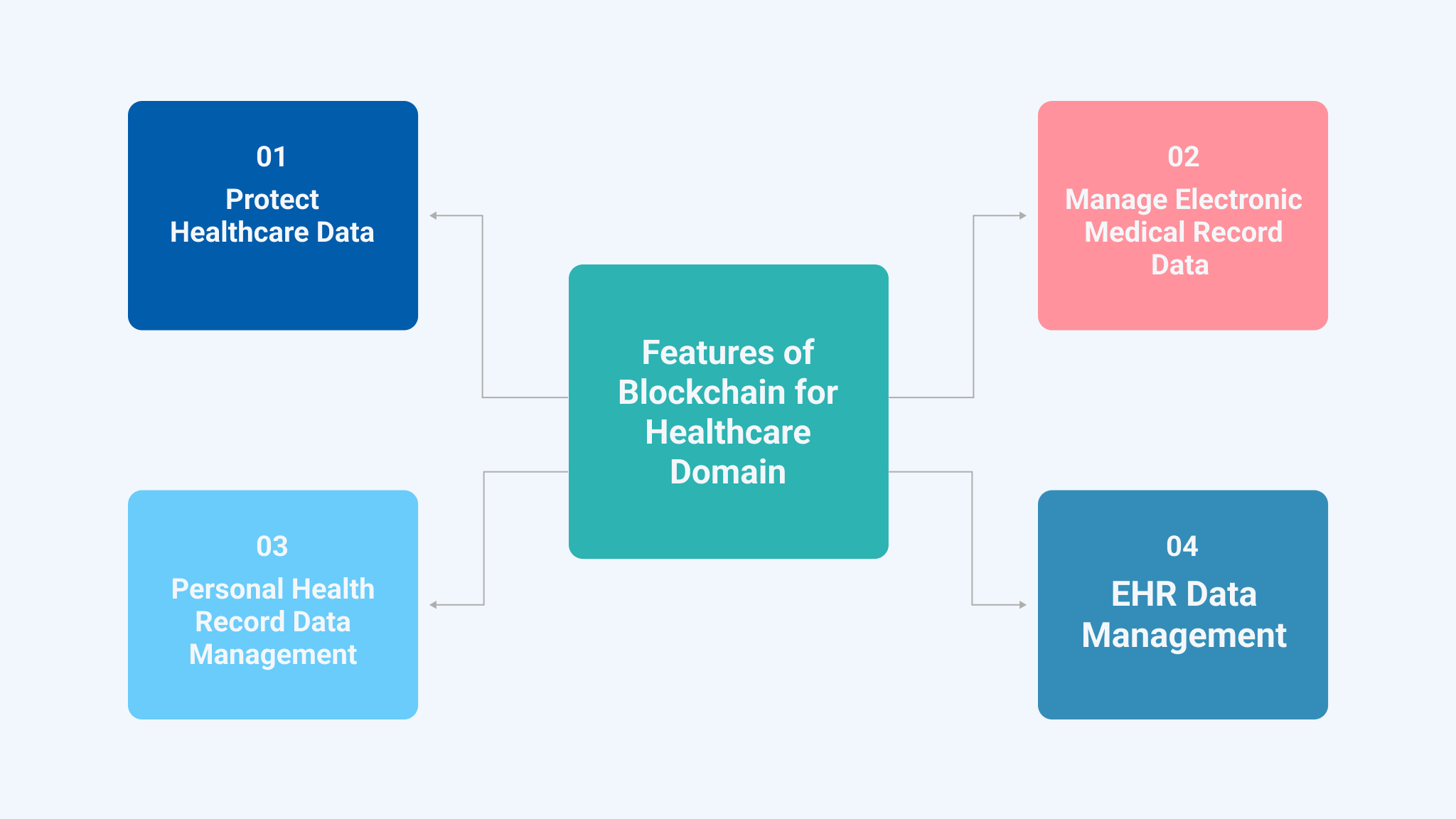
2. Blockchain Technology
The integration of blockchain technology in healthcare mobile applications emerges as a generative force, elevating the standards of security, privacy, and data management.
Blockchain ensures the security and integrity of health data, making it less susceptible to breaches. Blockchain can maintain an incorruptible, decentralized, and transparent record of all patient data well-suited for security in healthcare mobile applications.
Moreover, despite its transparency, blockchain ensures privacy by covering individuals’ identities through intricate and secure codes, safeguarding the sensitivity of medical data. The decentralized nature of this technology facilitates secure sharing of information among patients, doctors, and healthcare providers.
One notable example of blockchain technology usage in healthcare is in the management of electronic health records (EHRs). Blockchain can enhance the security, accessibility, and integrity of patient data.
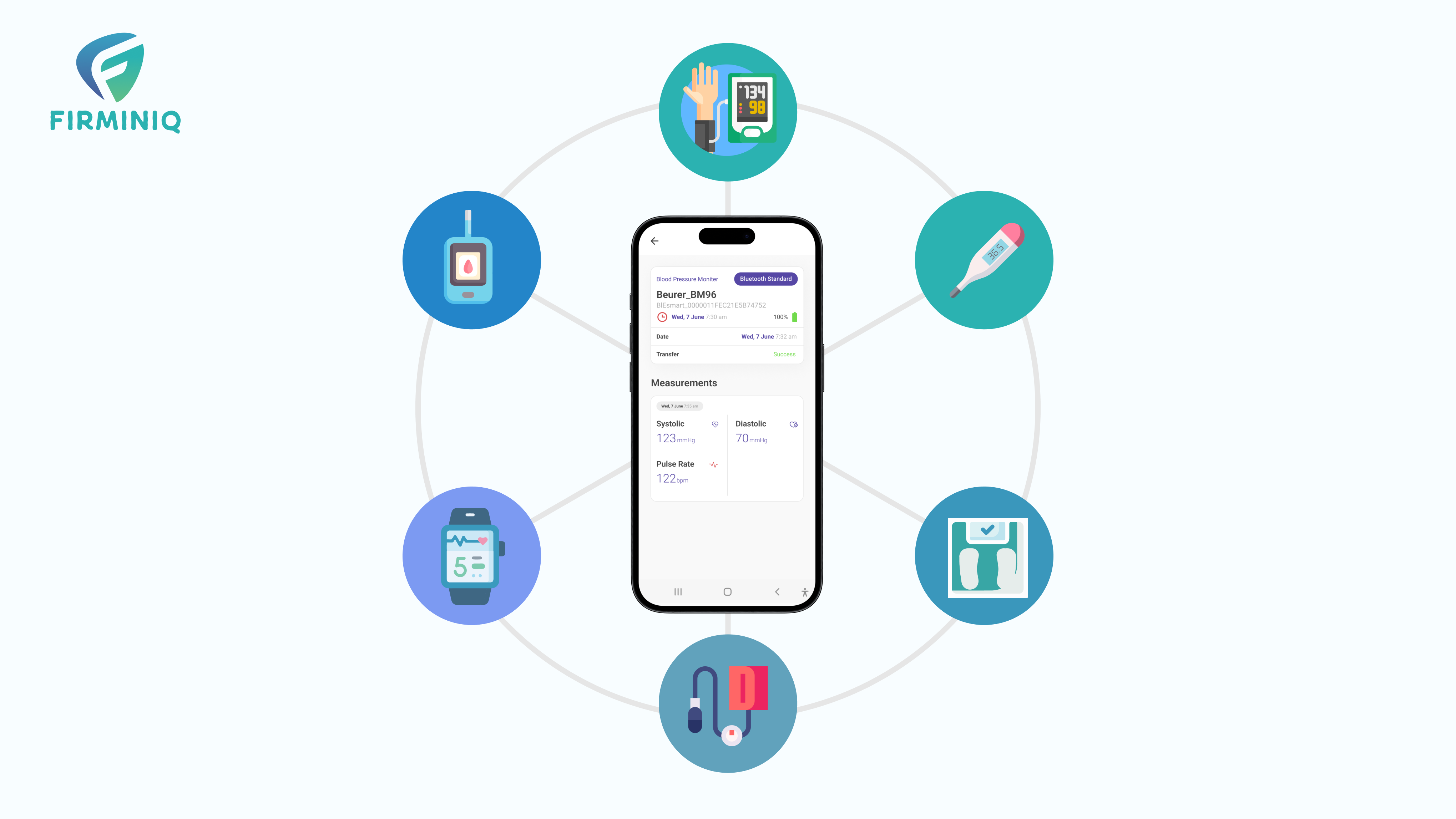
3. Wearables and IoT (Internet of Things) Integration
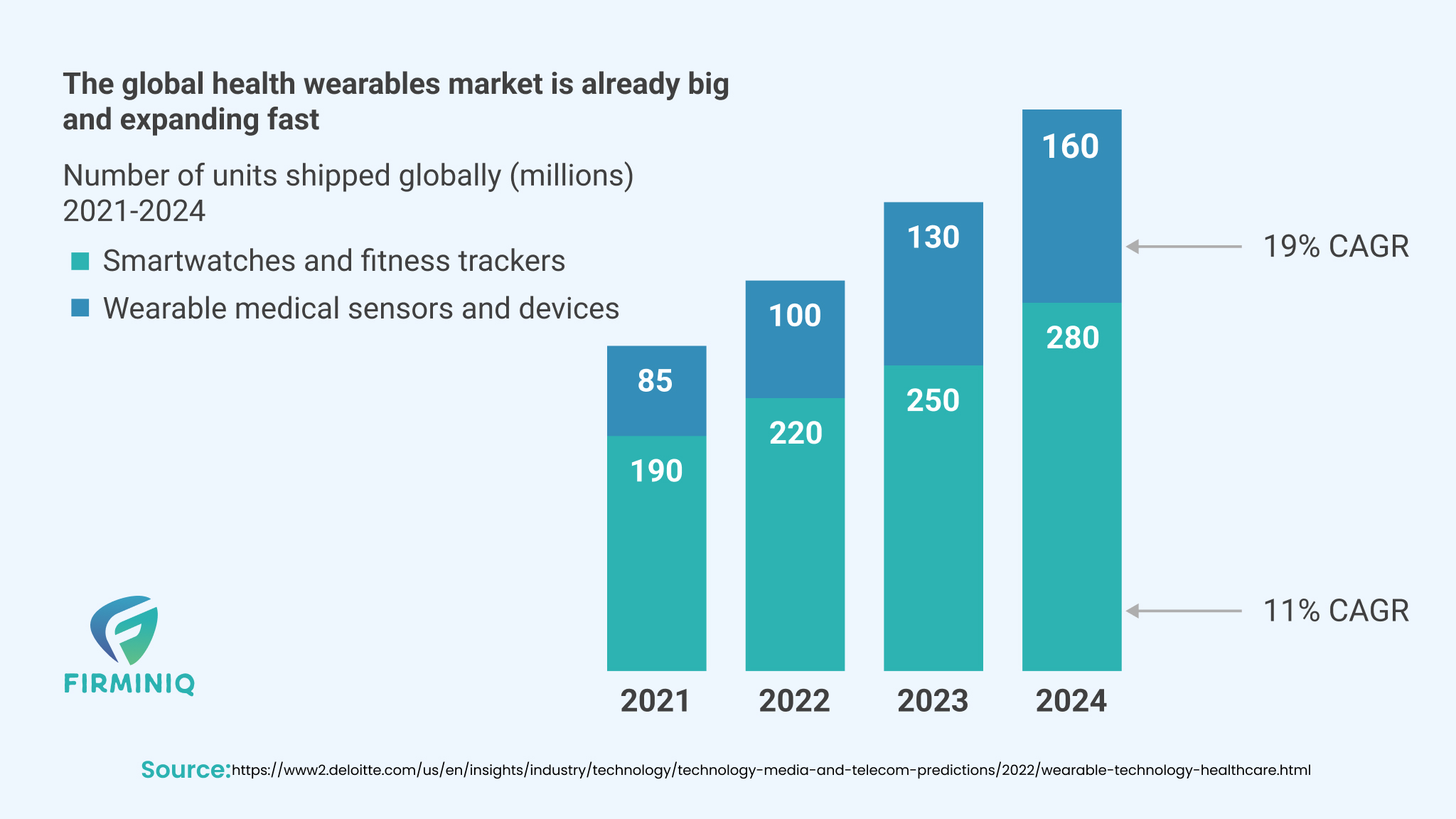
“Deloitte Global predicts that 320 million consumer health and wellness wearable devices will ship worldwide in 2022. By 2024, that figure will reach 440 million units.”- Deloitte Insights
There is an increased prevalence of wearables like smartwatches and fitness trackers that allow healthcare professionals to continuously monitor the vital signs and track the health metrics. The wearables and other IoT devices can be integrated into healthcare applications offering a complete picture of individual health records. Wearables are also used in RPM (Remote Patient Monitoring) as it helps patients to use these devices to track their health metrics at home, and the data is transmitted to healthcare providers in real-time through integrated applications.
The integration of wearables with healthcare applications contributes to a holistic view of an individual’s health. By combining data from various sources, such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and exercise routines, healthcare providers can assess overall well-being and make more informed decisions.
One of the examples includes a fitness tracker named Fitbit, as it uses sensors to monitor different health indicators like sleep patterns, calories burned, steps walked and more. The device is linked to smartphones that offer impactful insights.
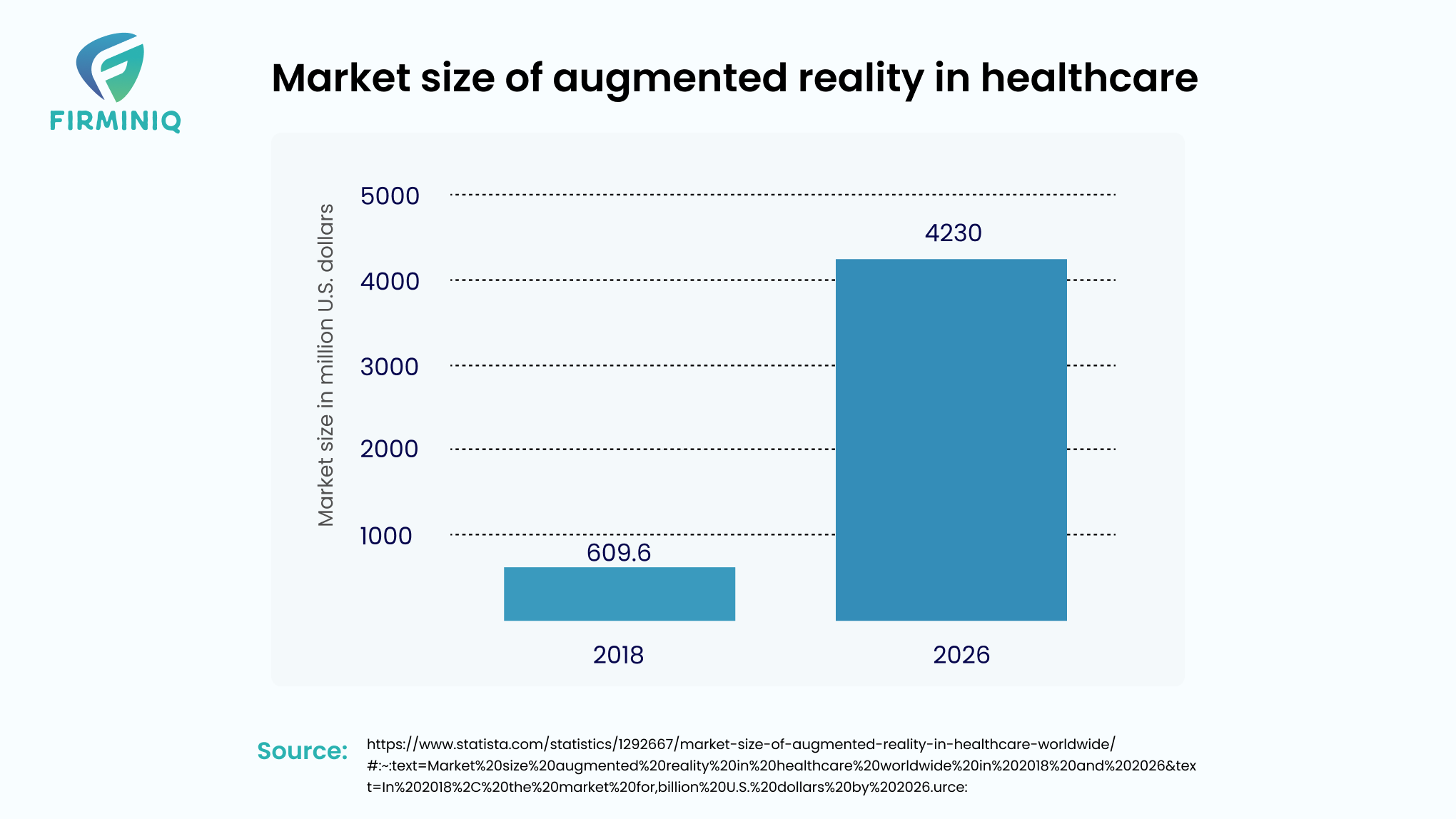
4. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
“In 2018, the market for augmented reality (AR) in healthcare worldwide was valued at around 610 million U.S. dollars. It is projected to reach more than 4.2 billion U.S. dollars by 2026.”- Statista
Integrating AR and VR technologies in healthcare mobile applications facilitate immersive experiences for patients, offering interactive 3D visualizations of medical conditions and treatment procedures. This growing awareness is fueling an increased demand for these technologies. With the usage of these immersive technologies in mobile applications, healthcare professionals can simulate surgeries, offer realistic scenarios, boost patient understanding of their conditions and a lot more.
5. Regulatory Support and Data Privacy
As healthcare apps navigate the complex landscape of regulatory requirements and data privacy, seamless integration of robust measures becomes paramount. Clear guidelines and regulations ensure the safety, efficacy, and ethical use of healthcare apps. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is crucial to maintaining patient trust and data security.
Robust data privacy measures, including encryption and secure authentication, are fundamental in healthcare app development. Trust in the security of personal health data is a cornerstone of successful mobile healthcare solutions.
Concluding Thoughts
The future of healthcare is linked with advancements in mobile application development. From leveraging Artificial Intelligence and blockchain for improved security to integrating wearables, these factors span a spectrum of advancements with their potential.
From leveraging innovative technologies to adhering to stringent regulations, the journey and future is of more empowerment, personalization, patient-centric, and more. As we stand on the verge of this healthcare revolution, the possibilities are boundless, and the future, as shaped by mobile app development, holds the promise of a healthier and more connected world.
Are you looking forward to developing a connected healthcare mobile application that is tailored to match your distinct requirements and aspirations accurately? Reach out to FIRMINIQ!