In the current era, cybersecurity threats are prevalent, so it becomes vital to protect susceptible data such as healthcare records, patient documents, and more. The potential consequences of cyber-attacks on healthcare organizations are not confined to technological disruptions alone; they resonate across multifaceted dimensions, casting a shadow on the core of connected healthcare systems.
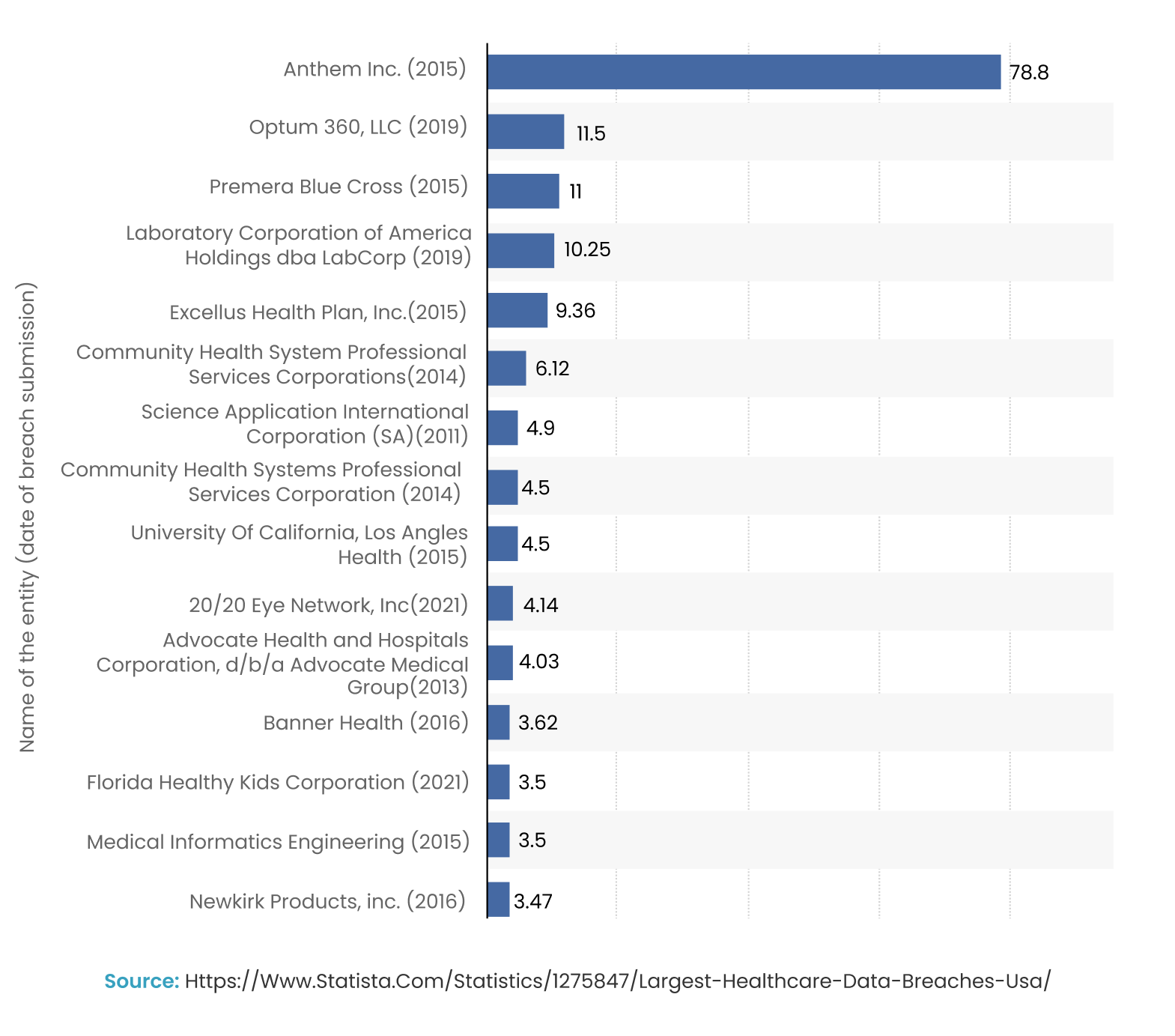
A concerning narrative unfolds the worrying healthcare data breach in the US. “The largest recorded U.S. data breach in the healthcare sector was in 2015 at Anthem Inc., a health insurance provider in the United States, when criminal hackers stole personal data affecting 78.8 million individuals.”- Statista
Here are the largest healthcare data breaches till date in the United States, with number of affected individuals.
The notable healthcare data breaches underscore the critical importance for organizations to prioritize both data security and efficient sharing of information.
By prioritizing such aspects and adopting a comprehensive approach for cybersecurity, organizations can navigate the complex landscape of connected healthcare information and its management. Adopting a comprehensive approach ensures the highest standards of data security and patient care.
Read further and explore the do’s and don’ts to navigate the intricate landscape of connected healthcare data and protect the integrity of patient sensitive information.
The Do’s and Don’ts of Healthcare Data Security in Healthcare
The potential consequences of a breach can be severe, impacting patient trust, legal compliance, and an organization’s reputation. To guide healthcare professionals and organizations, here are the essential do’s and don’ts of data sharing and security:
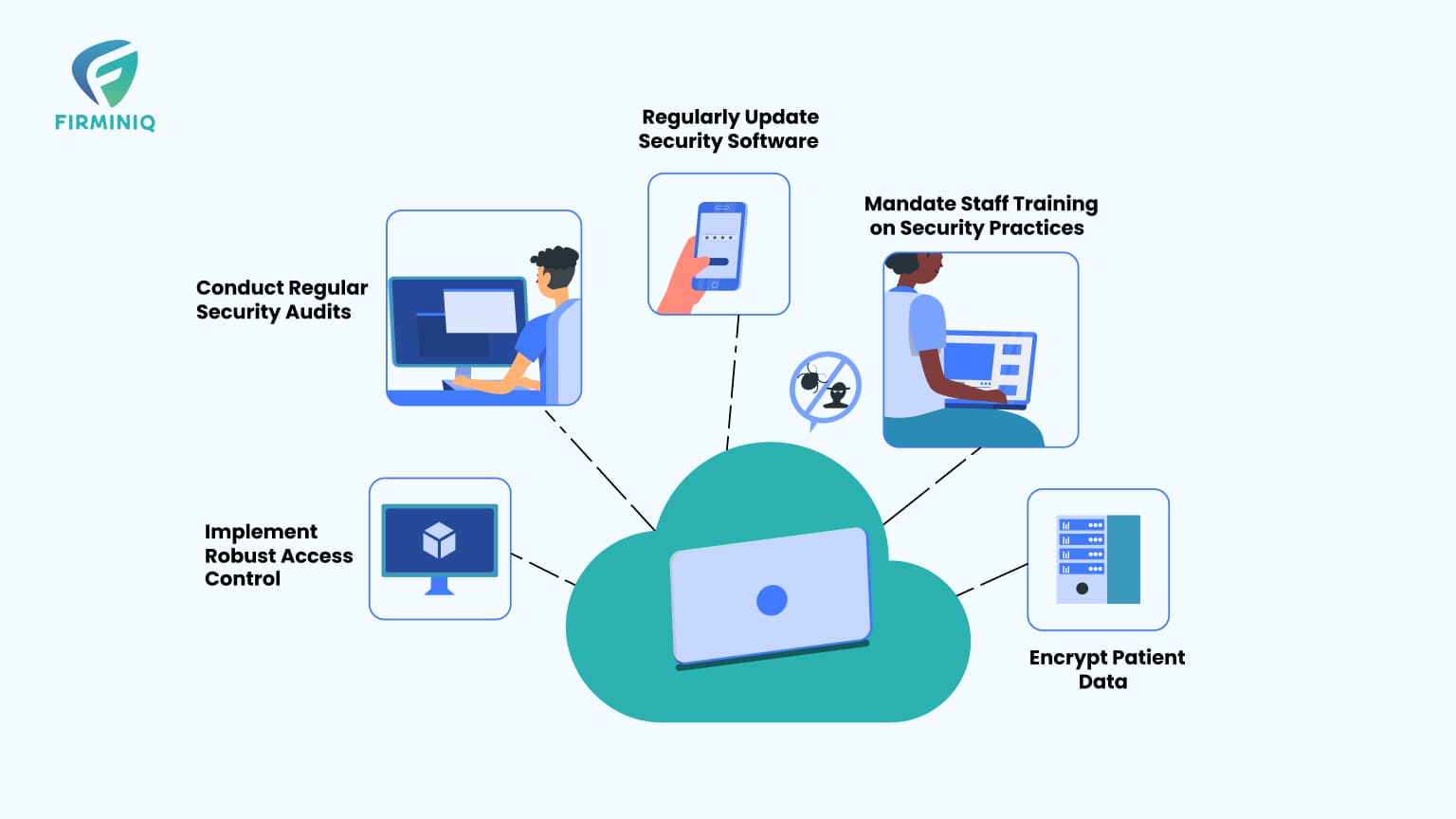
Do’s
1. Implement Robust Access Control
Implementing robust access control is a fundamental component of healthcare data security. It plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive information, ensuring patient privacy, and maintaining regulatory compliance. The robust access control ensures that only authorized individuals have access to patient information, records, and sensitive health information. It is necessary for maintaining patient privacy and their confidentiality.
Implementing robust access control is possible via role-based access control, user authentication and authorization, regular access audits, data encryption, and others.
2. Encrypt Patient Data
Encrypting patient data is a critical aspect of healthcare data security, offering a robust layer of protection against unauthorized access while ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive patient data. the attackers will be unable to decipher data without the encryption key. The attackers will be unable to decipher data without the encryption key.
Many healthcare regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, mandate the use of encryption to protect patient information. Compliance with these regulations helps avoid legal consequences and ensures to maintain patient trust.
3. Mandate Staff Training on Security Practices
Employees are the first line of defense against the security threats. Therefore, training healthcare individuals and employees helps recognize and respond to potential risks. Well trained and informed staff are less likely to compromise security because training sessions raise awareness about the potential insider threats and help employees understand their roles and responsibilities. It reduces the likelihood of security incidents caused by human errors.
4. Regularly Update Security Software
Keeping security software updated is vital to protect against evolving threats and vulnerabilities. Regularly updating the software is a proactive measure that defends the healthcare system against threats and vulnerabilities. The practice includes continuously checking and implementing updates for security components like firewalls, antivirus, and other measures. This process is crucial because it helps fix newly found weaknesses, patch existing issues, and make sure the security system is ready to protect against the latest cyber threats.
It is also vital to promptly update all the electronic devices, ranging from smartphones and computers to laptops and routers, with the latest available software versions.
5. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits is a paramount practice in healthcare to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of patient data. The audits allow healthcare organizations to identify vulnerabilities, save from breaches, ensure compliance with industry regulations, and manage risks.
“The biggest healthcare data breaches reported in 2021 each impacted more than 1 million patients, with more than 22.64 million patients affected overall.”- SC Media
With regular and well-defined audit schedules, healthcare organizations can assess various aspects of the system, networks, and processes.
The audit process should not be limited to identifying weaknesses but should extend to documenting findings and offering actionable recommendations for improvement. This documentation serves as a reference for future audits and assists in implementing necessary corrective actions.
Continuous improvement is a key takeaway from security audits. The iterative nature of this process allows healthcare organizations to adopt security measures and changes within the organization.
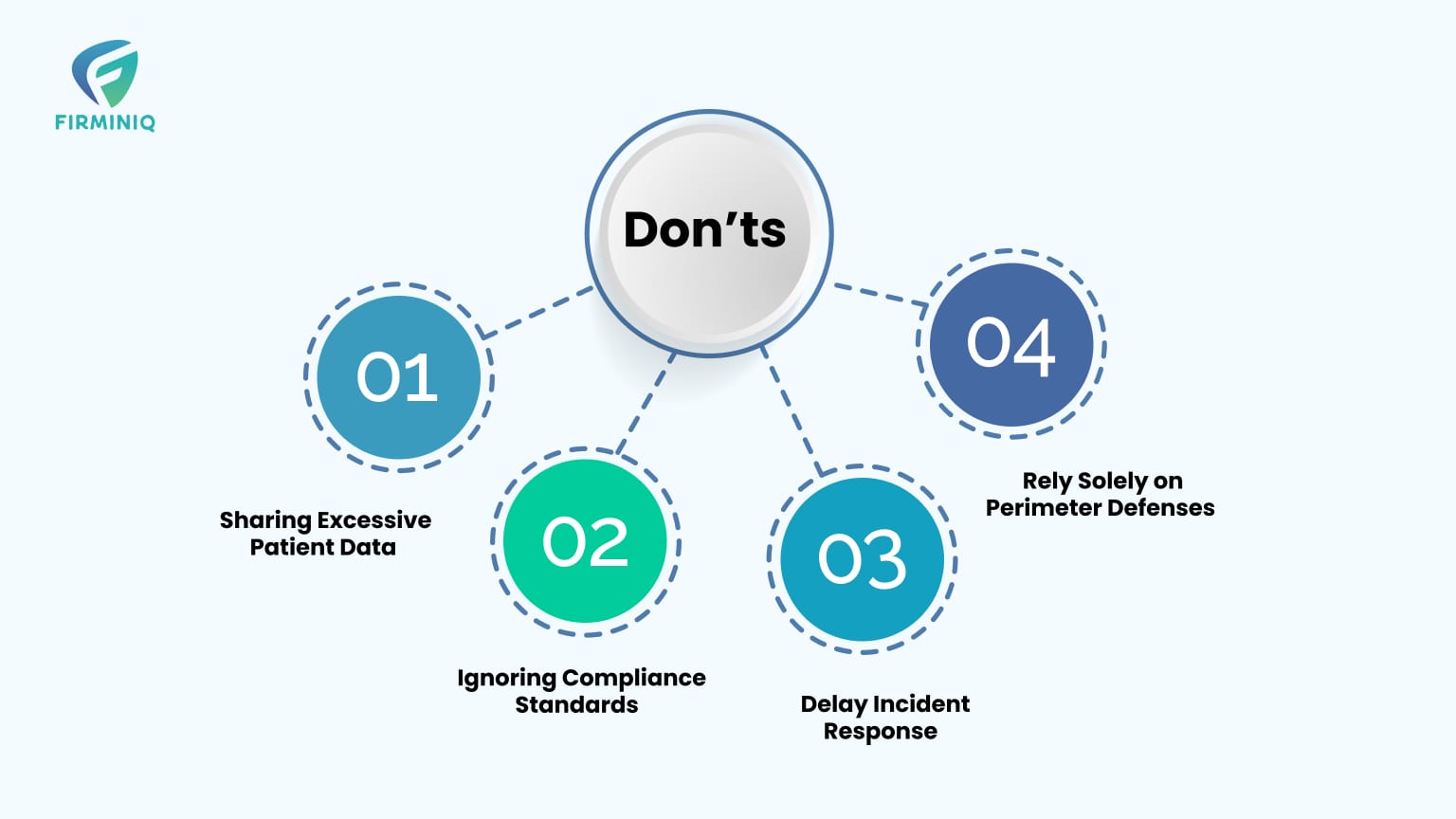
Don’ts
1. Sharing Excessive Patient Data
Excessive sharing of patient’s information without their consent may breach confidentiality. Excessive sharing increases the risk of unauthorized access to patient data. This could lead to data breaches, identity theft, or misuse of sensitive health information.
Patients trust healthcare providers with sensitive information, and any breach can corrode this trust, impacting their relationship.
2. Ignoring Compliance Standards
Healthcare operates under stringent regulations like HIPAA, GDPR and more that protect the patient’s data. Adherence to compliance standards is non-negotiable for safeguarding patient well-being, maintaining trust, and avoiding legal consequences.
3. Delay Incident Response
Postponing actions on incident response efforts is a detrimental practice, especially in healthcare. Delayed detection and response to security incidents allow breaches to potentially cause considerable damage.
If healthcare organizations neglect to prioritize a clear incident response plan and conduct drills, they face profound consequences in case of a security incident.
4. Rely Solely on Perimeter Defenses
Depending on perimeters like defenses, such as firewalls, can create a false sense of security within a healthcare organization. While firewalls play a crucial role in establishing a barrier between internal networks and external entities, depending exclusively on them might lead to overlooking other potential vulnerabilities and threats that can emerge from both external and internal sources.
Need Help with Ensuring Security of Healthcare Data?
Healthcare data is both a treasure and a target, therefore the call for continuous vigilance is vital. From embracing encryption to cultivating a culture of security and awareness, healthcare organizations must adapt and fortify their cybersecurity strategies.
Lacking adequate cybersecurity measures, such as relying solely on a security system or anti-malware software, exposes sensitive data to significant vulnerability in the event of a cyber-attack. One of the transformative forces is cloud computing in healthcare. The constructive interaction between cybersecurity practices and innovative capabilities of cloud technology ensures the efficiency of healthcare data management and more. If you are looking for more details on our cloud computing services in healthcare, reach out to us today!