In today’s healthcare landscape, ensuring the security of patient data within a cloud environment is paramount. Healthcare data security involves implementing stringent measures to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, or loss. These measures encompass encryption, comprehensive discovery and classification of cloud data assets, robust access controls, continuous monitoring, threat detection, and strict adherence to industry regulations. The objective is to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient data throughout its lifecycle—from storage and transmission to processing.
Why Healthcare Data Security Matters?
Healthcare data security is fundamental in our hyper-digital world, serving as a guardian to protect valuable and proprietary information from unauthorized access and misuse. As online transactions and interactions become more integral to daily life, ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive data is of utmost importance.
Cloud Security Strategies in Healthcare
Effective cloud security measures are essential for safeguarding healthcare data. Here’s how healthcare organizations can effectively implement these strategies:
1. Infrastructure Security
Cloud security focuses on ensuring the protection of healthcare data and applications that are hosted on remote servers managed by reputable cloud service providers.
It involves shared security responsibilities between healthcare organizations and cloud service providers, depending on the service model (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS).
2. Scalable Security Measures
Cloud security leverages highly scalable security measures provided by cloud vendors to protect healthcare data across multiple services and users.
3. Access Control and Identity Management
Cloud security utilizes robust identity and access management (IAM) controls to securely manage access to patient data and healthcare applications over the Internet
Healthcare providers must ensure that patient data remains confidential, intact, and accessible only to authorized personnel. As healthcare increasingly adopts cloud computing for its efficiency and flexibility benefits, implementing robust security measures becomes crucial to mitigate risks associated with storing and processing sensitive information.
Top Threats to Healthcare Data Security in Cloud Computing
Cyber threats continue to evolve, posing significant challenges to healthcare organizations. Key threats include:
1. Misconfigured Cloud Infrastructure: Vulnerabilities arising from improperly configured cloud environments leading to data exposure.
2. Account Hijacking and Unauthorized Access: Unauthorized access to sensitive healthcare data through compromised accounts or credentials.
3. Lack of Visibility and Control: Inadequate oversight of data flows within the cloud environment increases the risk of data breaches.
4. Weaknesses in Identity and Access Management (IAM): Mismanagement of IAM policies resulting in unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
5. Unsecured APIs and Network Connections: Vulnerable APIs and insecure network connections serve as potential entry points for cyber attackers.
6. Lack of Encryption: Failure to encrypt data both at rest and in transit leaves patient data susceptible to interception and theft.
Cloud data security is fundamental to establishing trust in the digital age. It integrates technologies, processes, and policies—such as encryption, access control, continuous monitoring, and backup and recovery procedures—to protect healthcare data, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining data security.
Cloud Data Security Challenges
Ensuring robust cloud data security is critical as organizations increasingly store and process sensitive information in cloud environments. The consequences of a data breach can be severe, ranging from the loss of sensitive data to financial repercussions and reputational damage. Cybercriminals target vast amounts of sensitive information stored in the cloud, underscoring the need for organizations to prioritize cloud security measures.
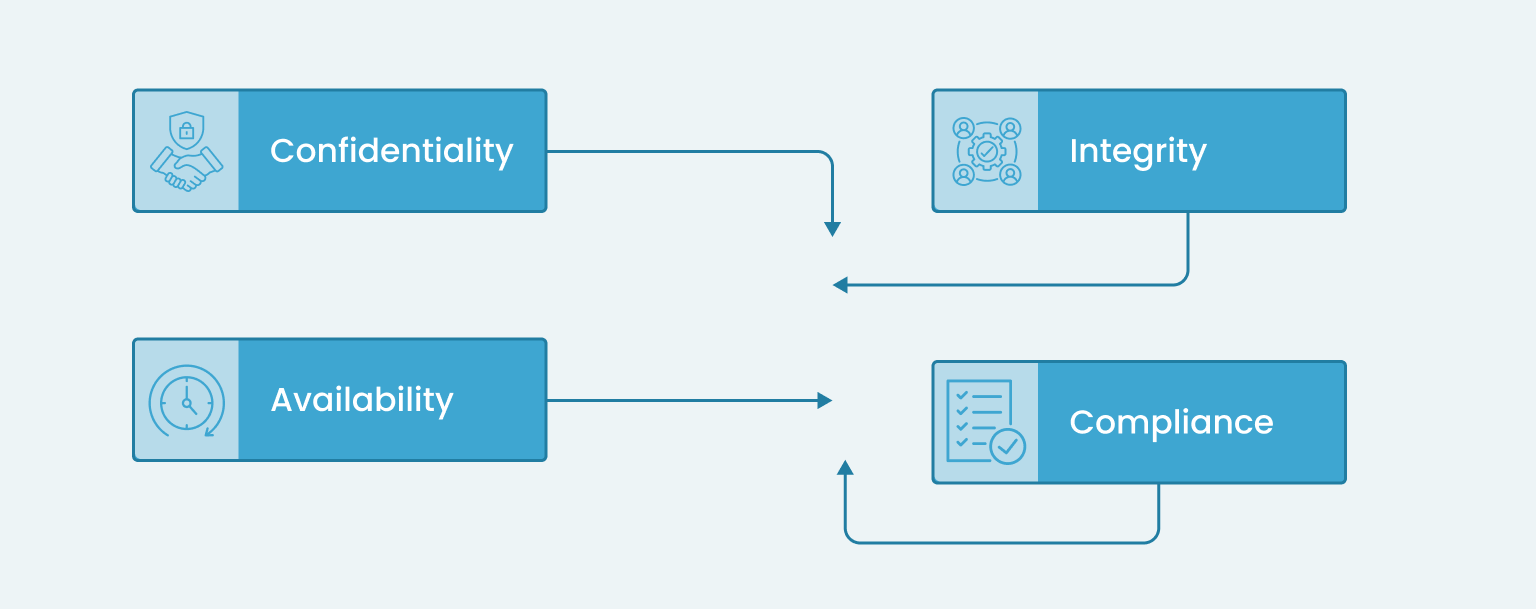
Organizations must adhere to the following principles to mitigate cloud data security challenges:
1. Confidentiality: Protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and disclosure through robust encryption and access control measures.
2. Integrity: Ensure data remains accurate and trustworthy throughout its lifecycle in the cloud, implementing regular validation and integrity checks.
3. Availability: Guarantee data accessibility to authorized users as needed, utilizing robust backup and recovery mechanisms for data availability during security incidents.
4. Compliance: Adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) governing data processing and storage practices to minimize regulatory risks.
As organizations navigate the complexities of cloud data security, adopting proactive measures—such as comprehensive security controls, advanced monitoring solutions, and effective incident response plans—enhances resilience against evolving cyber threats in the cloud. Safeguarding data integrity, confidentiality, and availability remains essential to maintaining trust and operational continuity in the digital era.
Cloud Data Security Best Practices
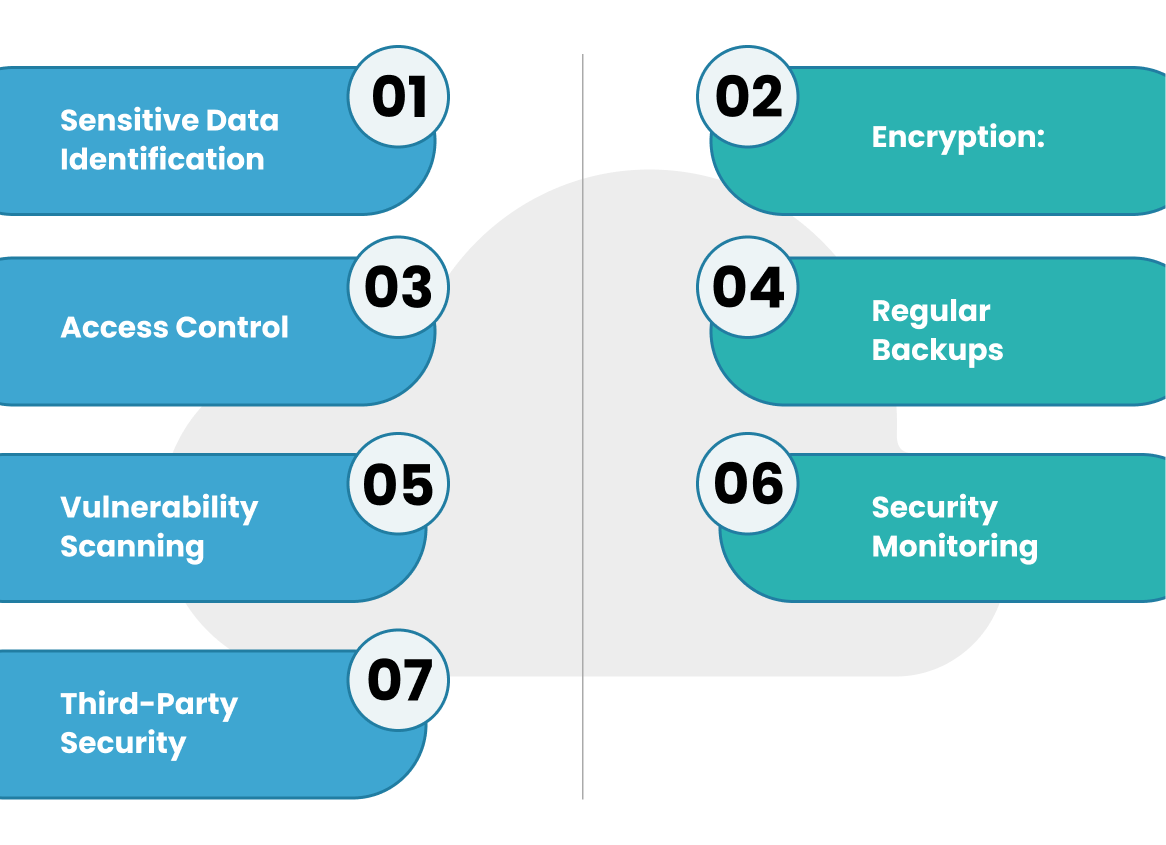
To enhance healthcare data security in the cloud, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
1. Sensitive Data Identification: Identify and classify sensitive healthcare data to apply appropriate security controls.
2. Encryption: Encryption ensures sensitive data is securely encoded during both transmission and storage, preventing unauthorized access.
3. Access Control: Implement stringent access policies, including role-based access and multi-factor authentication, to restrict access to sensitive healthcare data.
4. Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of healthcare data stored in the cloud to ensure data availability and recovery in case of security incidents.
5. Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning involves regularly conducting assessments of cloud infrastructure to identify and address potential security risks effectively.
6. Security Monitoring: Implement robust security monitoring and analytics tools to promptly detect and respond to security threats.
7. Third-Party Security Audits: Regularly audit and assess security practices of third-party vendors managing cloud services to ensure adherence to security standards.
By adopting these best practices, healthcare organizations can proactively mitigate risks and protect sensitive patient data in the cloud environment.
Conclusion
Healthcare data security in a cloud-first world is essential for maintaining patient trust and regulatory compliance. Robust cloud security measures empower healthcare organizations to securely store, process, and transmit sensitive information, supporting operational efficiency and quality patient care.
Investing in cloud data security not only protects sensitive data against cyber threats but also enhances organizational resilience and competitiveness in the digital healthcare landscape. Embracing cloud data security as a strategic imperative ensures healthcare organizations can innovate and deliver quality care while safeguarding patient privacy and security.