There is a widespread rise in the number of patients suffering from chronic diseases including diabetes, heart strokes, respiratory conditions, and more. These conditions pose substantial challenges for those affected, impacting the quality of life, while requiring ongoing care. “An estimated 129 million people in the US have at least 1 major chronic disease (e.g., heart disease, cancer, diabetes, hypertension)” as defined by the US Department of Health and Human Services.
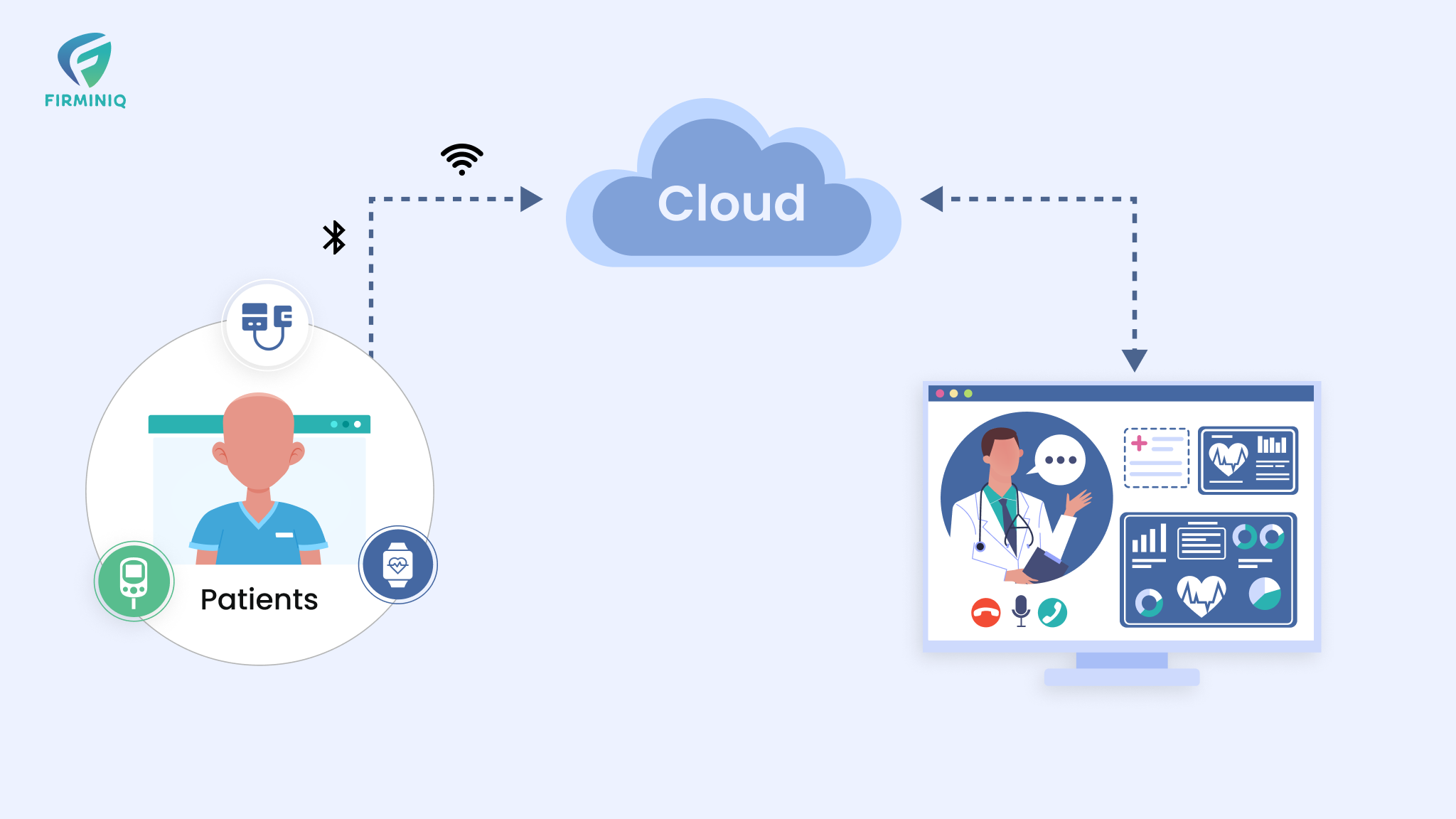
Connected healthcare devices offer opportunities for continuous monitoring, proactive care, and enhanced patient engagement, reducing illness impact. These devices include wearables, sensors, remote patient monitoring devices, and more, which collect healthcare data in real-time and offer continuous monitoring. Offering patients and healthcare providers actionable insights and vital tracking in real-time allows timely intervention and more personalized care. The blog helps you explore how connected health tools empower patients for chronic care management.
Impact of Connected Health Tools on Modern Healthcare
Connected healthcare devices revolutionize the way chronic diseases are managed. The devices help patients monitor their health conditions from the comfort of their homes and offer valuable insights to both the patients and physicians. From smart watches to sensors and remote monitoring devices, the tools offer real-time data to the patients and the healthcare teams. Let us explore the benefits of connected health tools in chronic disease management.
Benefits of Connected Health Tools for Chronic Patients
1. Real-Time Data Collection
Real-time data is beneficial for patients with chronic diseases as it offers a constant stream of information about their health condition. The connected healthcare tools offer real-time data tracking of vitals and health parameters at regular intervals.
For example, if a patient is suffering from hypertension, a digital blood pressure monitor can track their blood pressure at regular intervals. The device sends data to a mobile app, where the patient and the healthcare provider can monitor trends and identify any alarming changes.
2. Proactive Health Management
Connected healthcare tools detect early signs of deteriorating health and notify patients and healthcare providers if there are any fluctuations. By continuously monitoring health metrics, physicians can timely intervene and ensure there are no complications in the management of disease.
For example, smart glucose monitoring trackers can help diabetic patients track their blood sugar levels, allowing physicians to inform them if the levels are too low or high. In that case, patients can immediately take necessary steps and preventive measures like medications or insulin to eliminate conditions like hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
3. Enhanced Patient Engagement
As the patients become active participants in managing their own health via connected health tools, they are more motivated to take control of their well-being. With access to the health data and feedback, they can better adhere to the treatment plans, modify lifestyle, and improve the outcomes.
For example, a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) uses a connected spirometer to monitor the functionality of the lungs. The device records data on lung capacity and airflow, which the patient can view on a mobile app. This visibility into their health status encourages the patient to follow prescribed respiratory therapies, avoid triggers, and support a healthy lifestyle.
4. Medication Adherence
Connected healthcare devices help patients to improve their medication adherence. The mobile applications help patients send automated messages and reminders to the patients to take their medications at the time prescribed by the physician. These alerts can be modified by the patient or their family members while ensuring the reminders remain convenient and effective. The information can be further shared with the healthcare provider for review. Also, the use of devices like smart pill dispensers can help the patient get the correct dosage of medication while reducing the risk of missed/incorrect dosage.
For example, a patient with diabetes can use a connected pill dispenser that helps them track when the dose is taken, reminds them of the dosage and sends all information to the mobile apps, allowing them to track all the details.
5. Convenience and Cost-Savings
With connected healthcare tools, patients can leverage convenience and cut down costs. Patients can have virtual consultations (video calls/audio calls/chat) with their healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes, which offers them convenience and prevents them from traveling to the hospitals and waiting in queues to see the doctor.
Effective management of chronic conditions via connected tools reduces the frequency and severity of disease outbreaks while minimizing the overall need for acute care. As there are reduced hospitalizations and visits to the clinics, the tools also contribute to significant cost savings.
Use Cases for Connected Health Devices
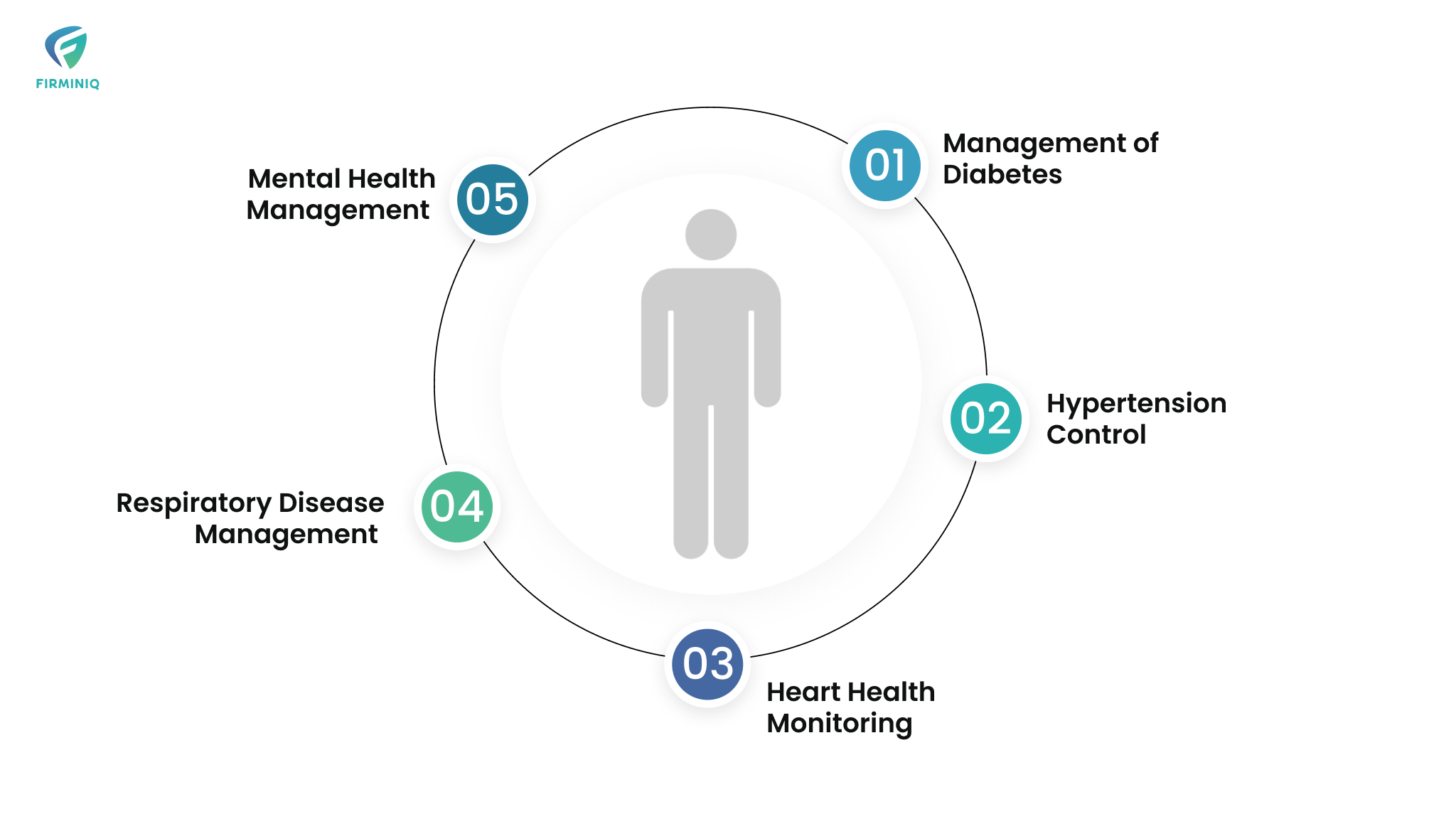
Having mentioned the benefits of connected health tools, let us now focus on impactful use cases of these tools and how they manage chronic conditions and improve health outcomes.
1. Management of Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases that significantly impacts healthcare systems. Patients suffering from diabetes can use Bluetooth-enabled digital scales (Wi-Fi) that help them measure their body weight. The data is transmitted to the healthcare provider where they seamlessly analyze the trends, recommend treatment plans to the patients, and assess the effectiveness of the patient’s weight loss program.
A study from the National Library of Medicine highlights the effectiveness of connected health tools, and self-monitoring devices and technologies in managing diabetes for individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The evidence supports that self-monitoring of blood glucose remains a critical tool in diabetes management, contributing to better health outcomes.
2. Hypertension Control
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly half of all adults in the United States (47%) have hypertension, highlighting the urgent need for effective management strategies. For the patients to manage their blood pressure, using Bluetooth-enabled blood pressure monitors helps monitor response. The device simply records the readings and transmits them with minimal effort. Healthcare providers can monitor the blood pressure trends of the patient over time and warn them about the dangerous spikes that may require immediate attention.
3. Heart Health Monitoring
“The global burden of heart failure (HF) continues to rise, affecting at last 26 million people as of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality globally.”- National Library of Medicine
Smart ECG monitors and other wearable devices help continuously track heart rate and detect any irregularities. The devices transfer the data in real-time to the cardiologist and enable early detection of cardiac events. With timely intervention, cardiologists can help patients and prevent heart attacks, strokes, and more while improving patient outcomes and reducing emergency hospital visits.
Also, a study from Circulation depicts that mHealth tools show promising potential in improving lifestyle behaviors and management of cardiovascular diseases globally. Evidence supports their effectiveness in developed countries for addressing risk factors such as weight, smoking, and physical activity, and managing conditions like hypertension, hospital readmissions, and diabetic glycemic control.
4. Respiratory Disease Management
“The number of COPD cases globally among those aged 25 years and older will increase by 23% from 2020 to 2050, approaching 600 million patients with COPD globally by 2050.”-JAMA Network Open
Patients with respiratory diseases like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and others need effective management of symptoms and detection before worsening. Tools like wireless spirometers help measure lung function by recording parameters like lung capacity and airflow. Healthcare providers can further analyze the data, identify triggers, and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Tools like smart inhalers track medication dosage and remind patients to adhere to their medication schedules.
5. Mental Health Management
As per CDC, about 1 in 25 U.S adult’s lives with a serious mental illness, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or major depression.
Connected health tools play a critical role in managing mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, and others. The mood and health tracking apps allow patients to track the patient’s mood, sleep patterns, and other activities. The data collected helps identify the patterns that affect mental health. With connected healthcare tools, patients can leverage a convenient way to receive care without having to visit the clinics physically.
Epilogue
The world of RPM and connected healthcare has transformed how traditionally chronic conditions were managed. The tools offer continuous tracking of vitals and health condition monitoring, and the devices empower patients to conquer chronic conditions and live better lives. Also read, Conquering Chronic Conditions: A Holistic Approach to Management with RPM.
As we continue to advance, the use of these devices will only become more significant. Want to harness the power of devices to revolutionize chronic disease management? Let us help!