What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing, often called pen testing, is a method used to evaluate the vulnerabilities and weak points of a security system.
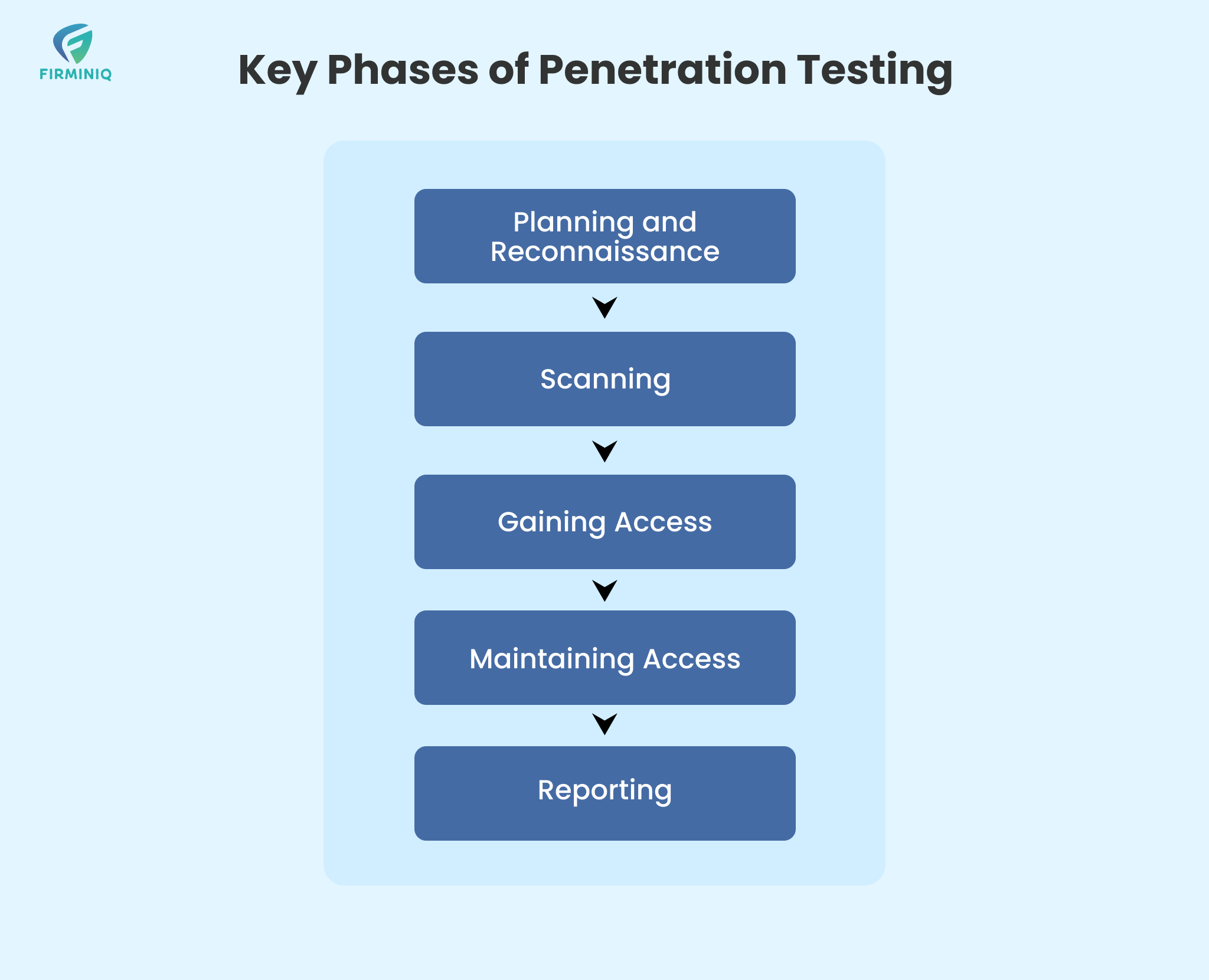
It helps organizations detect potential security gaps and understand associated risks. This testing process typically involves five key phases:
- Planning and Reconnaissance
- Scanning
- Gaining Access
- Maintaining Access
- Reporting
Importance of Penetration Testing
- Specifically targeted, where attackers, often referred to as hackers, have a deep understanding of the security defenses and system operations. This knowledge allows them to execute more effective attacks. On the other hand, random attacks aim to probe an organization’s defenses to identify vulnerabilities that can be exploited later in more targeted attacks. These cyberattacks vary significantly in their methods, impacts, and associated risks.
- Even the most security-conscious organizations cannot eliminate the risk of being targeted. As businesses expand and migrate to cloud environments, their dependence on the internet increases, making them more susceptible to cyberattacks. Preparing for these threats 24/7 has become a necessity.
- In this context, penetration testing is a crucial practice. It plays a key role in helping organizations assess their defenses and is considered an essential part of maintaining robust security practices.
Penetration testing can be particularly valuable for:
- Protecting crucial financial and sensitive information during network transmission.
- Meeting client requirements, as many now insist on penetration testing as part of the software release process.
- Identifying system vulnerabilities and understanding the risks associated with potential attacks.
- Strengthening security strategies within organizations.
Why is Penetration Testing Crucial?
With the increasing frequency of cyberattacks, organizations need to remain vigilant around the clock. Penetration testing plays an essential role in ensuring that businesses are prepared to defend against potential threats. As organizations expand and migrate to cloud environments, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. This necessitates continuous monitoring and testing to mitigate the risk of breaches.
Benefits of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing offers several key benefits, including:
- Protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical assets.
- Assessing device security configurations.
- Supporting organizations in identifying and addressing cyber threats.
- Verifying the implementation of new security measures.
- Offering a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s security framework.
- Ranking vulnerabilities according to their potential impact on business operations.
- Enabling proactive risk management to avert attacks.
- Safeguarding an organization’s reputation and strengthening customer trust.
- Mitigating the risk of data breaches.
- Measuring the effectiveness of security defenses.
- Supporting business continuity efforts.
- Detecting previously unnoticed vulnerabilities and simulating real-world attack scenarios.
Penetration Testing Tools
Some popular penetration testing tools include:
• Metasploit: A widely used penetration testing framework that assists security teams in managing security assessments. It features a user-friendly graphical interface and is compatible with Mac OS X, Windows, and Linux. Metasploit is free to use.
• BeEF (Browser Exploitation Framework): This tool tests web browsers and helps testers explore security issues beyond the client system.
Types of Penetration Testing
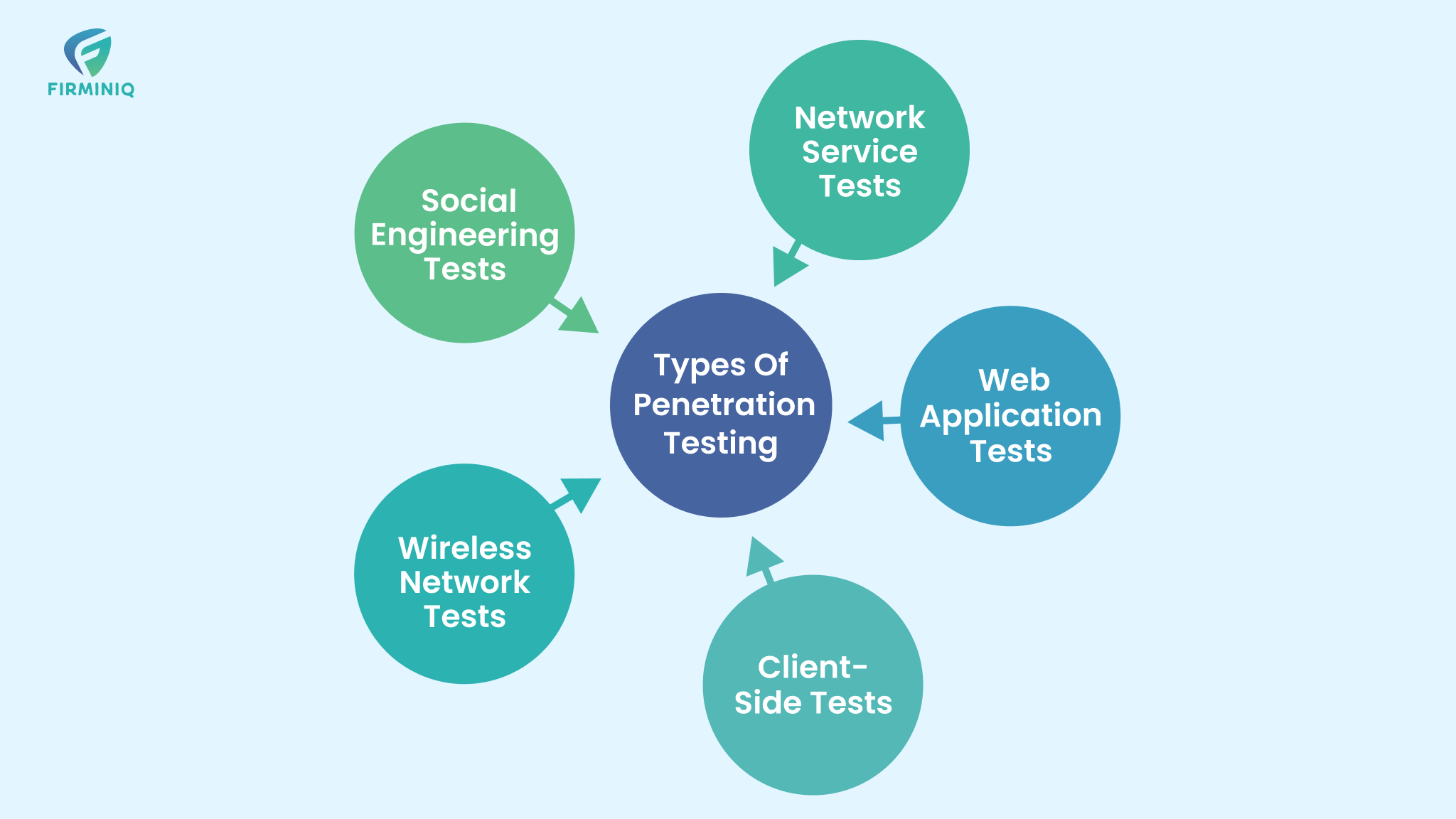
Different types of penetration testing are employed depending on the specific security concerns:
- Network Service Tests: Focus on identifying vulnerabilities in the client’s network infrastructure, including firewall configuration and DNS-level attacks.
- Web Application Tests: Involve detailed assessments of web applications and components such as ActiveX, applets, and scriptlets.
- Client-Side Tests: Examine local security threats in applications like web browsers, Git clients, and media players.
- Wireless Network Tests: Target wireless devices like smartphones and tablets, as well as the protocols that configure wireless networks.
- Social Engineering Tests: Simulate attacks that might be initiated by insiders within an organization, including both remote tests (e.g., phishing email campaigns) and physical tests (e.g., attempts to gather sensitive information through intimidation).
What is Ethical Hacking?
An ethical hacker is a cybersecurity expert who intentionally probes into applications, systems, or networks to identify vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited by malicious hackers. The primary goal is to uncover these security flaws so that they can be addressed before they are discovered and used for nefarious purposes. Ethical hackers employ similar techniques as malicious hackers, such as phishing attacks, password cracking, and system configuration exploitation.
Ethical hackers typically participate in evaluating the security of new applications or systems prior to their release into the production environment.
Types of Ethical Hacking:
- Web Application Hacking
- Social Engineering
- System Hacking
- Hacking Wireless Networks
- Web Server Hacking
Common Tools Used in Ethical Hacking:
Acunetix
- Platform: Windows, Mac, RedHat 8, Web-based
- Purpose: Comprehensive web security scanning
- Features: Acunetix automates the process of web security testing to detect vulnerabilities like SQL Injection and Cross-site Scripting.
- This tool is proprietary software and is not available as open-source
Netsparker
- Platform: Windows, Web-based
- Purpose: Automated application security testing
- Features: Netsparker identifies and reports security issues, including SQL Injection and Cross-site Scripting, with high accuracy.