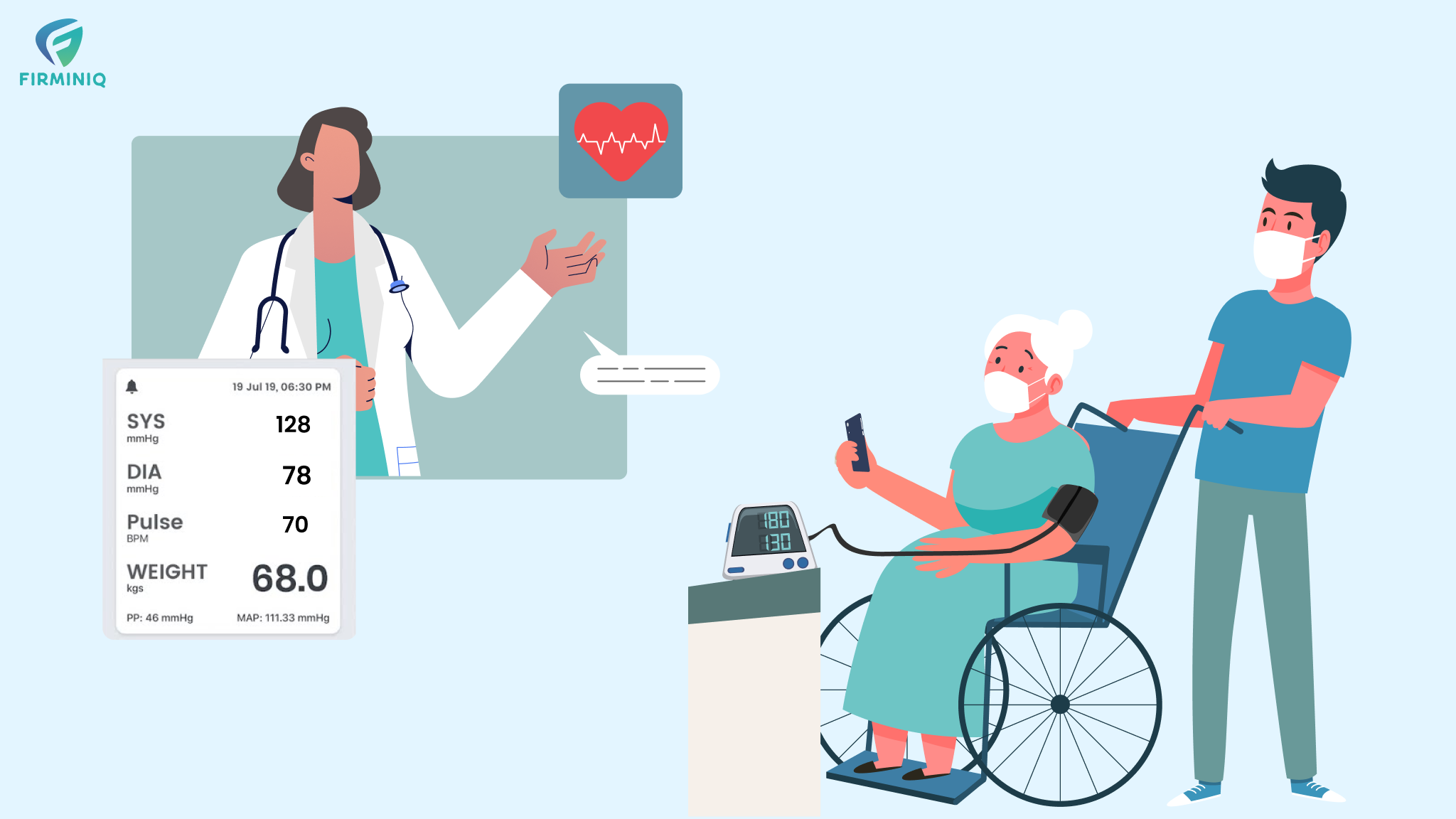
Remote patient monitoring is transforming healthcare delivery, especially with advancements in technology and a growing demand for more patient-centered healthcare services. One of the key elements enhancing RPM (Remote Patient Monitoring) is the integration of biomarkers.
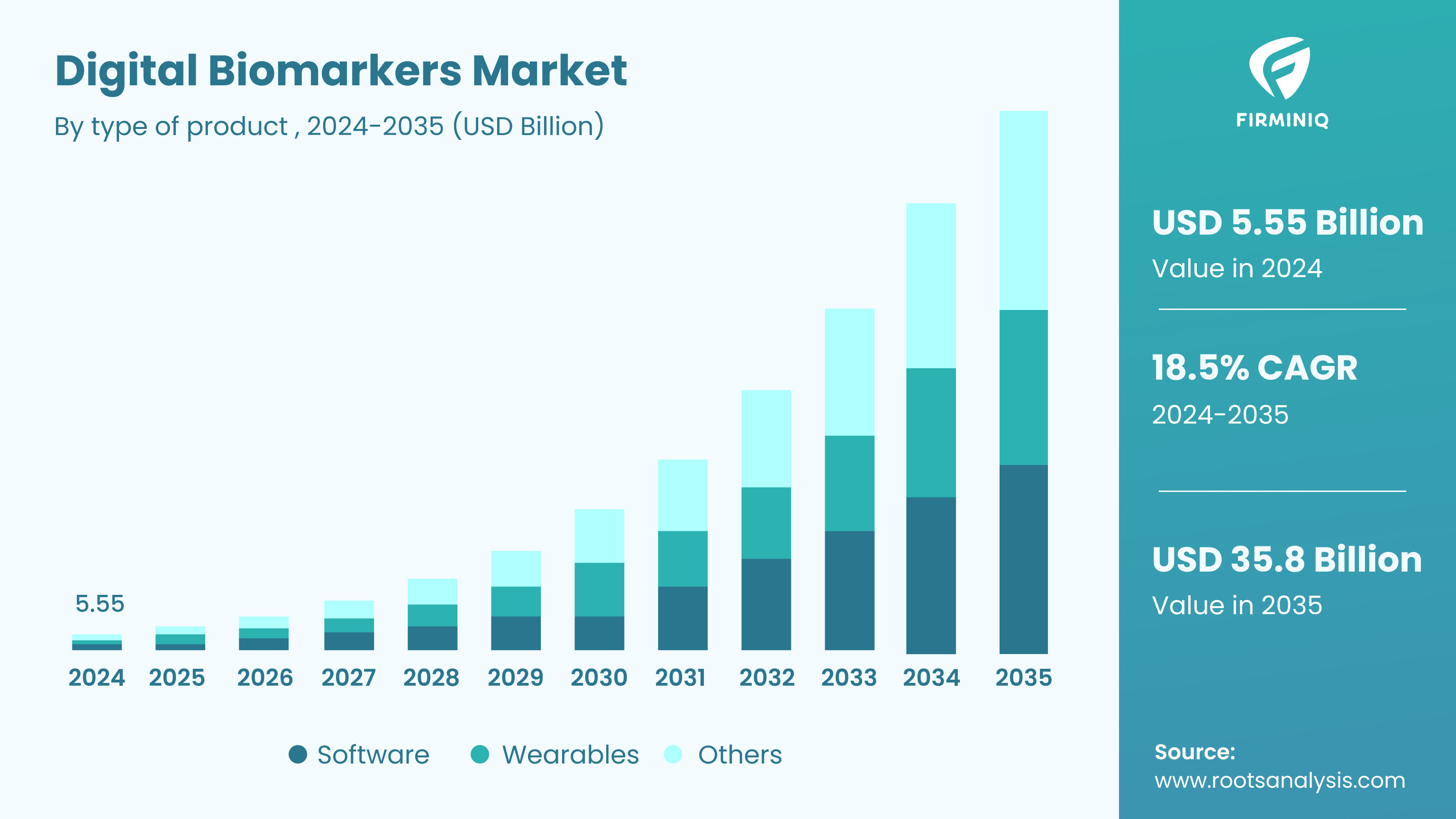
As per Root Analysis, “With the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, growing emphasis on remote patient monitoring, and continuous advancements in the technologies, the digital biomarkers market size is prepared for growth, in the foreseen future. The digital biomarkers market is estimated to be worth USD 5.55 billion in 2024 and will reach USD 35.8 billion in 2035.”
The statistics depict that RPM stands out as a key driving force behind this growth, along with the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and continuous technological advancements. Detecting changes in biomarker levels allows physicians to detect patient problems at an early stage and intervene timely. Also, for chronic patients, the biomarkers offer continuous monitoring and prevent complications. Biomarkers have a multifaceted role in RPM and healthcare organizations or physicians can seamlessly leverage data from biomarkers and offer patient-centered care. The blog covers all the information about the role of biomarkers in RPM and how harnessing it allows providers to achieve the outcomes. But, before we talk about the role of biomarkers, let us understand what exactly biomarkers are.
What Exactly are Biomarkers?
Biomarkers refer to measurable physiological and behavioral indicators collected via devices, wearables, apps, biosensors, biological samples and more to offer insights into the patient’s health status. They offer information that complements traditional vital sign monitoring and patient-reported data in RPM. From offering insights into disease trends, to treatment effectiveness and more, biomarkers offer a holistic view of health and empower data-driven interventions. By harnessing biomarker data in an RPM solution, healthcare providers can ensure early symptom detection, enhance patient care, deliver personalized care, and more.
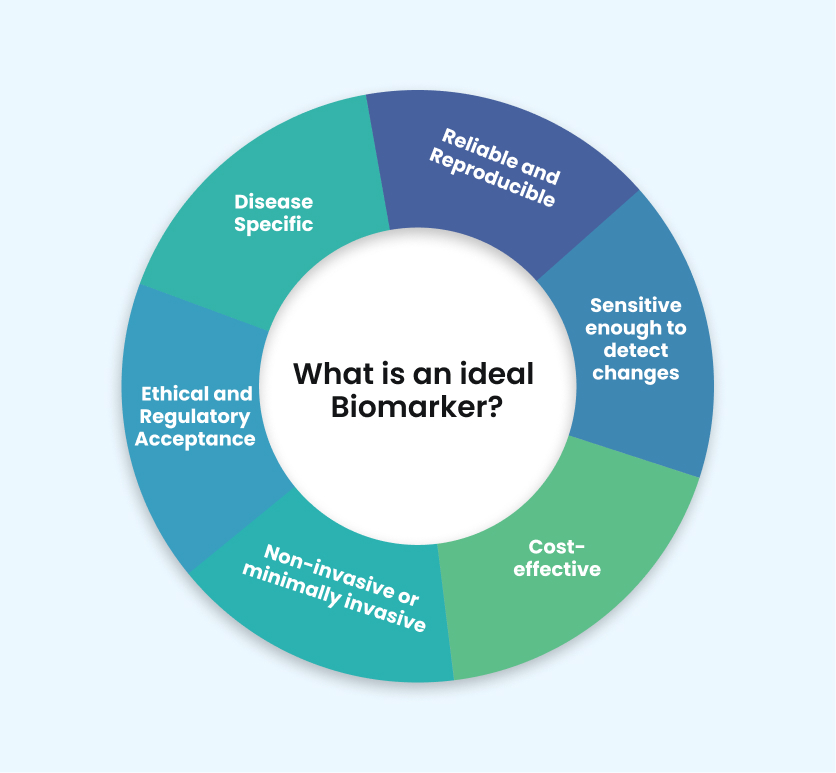
An ideal biomarker is a specific, sensitive, and reproducible measure that provides clear insights into biological or pathological processes. One example of biomarkers is Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA), used for prostate cancer that has high specificity and is sensitive to prostate conditions. Higher PSA levels in the blood indicate the presence of prostate cancer, even if there are no symptoms detected. It therefore allows for early detection and treatment.
Classification of Biomarkers for Easy Monitoring
Biomarkers in RPM play a vital role in tracking data for healthcare providers while offering timely intervention and improved outcomes for patients. Here are the biomarkers classification in RPM:
1. Physiological Biomarkers
These are the biomarkers indicating the patient’s health status, monitored by wearables, devices, or sensors. The biomarkers offer real-time data that enables healthcare professionals to monitor and manage the patient’s condition. Monitoring patient’s conditions like heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, body temperature, and others are physiological biomarkers that offer real-time insights of the patient’s health.
2. Biochemical Biomarkers
It is another category of biomarkers that are indicators of molecular mechanisms and measured via bodily fluids like blood, urine, or saliva. Whether it is about analyzing blood glucose level, lipid profile, electrolytes, hormones, biochemical biomarkers offer invaluable insights into various physiological and pathological conditions. In the RPM realm, these biomarkers can be accessed via diagnostic devices and other advanced technologies while offering real-time data for efficient patient management.
3. Behavioral and Activity Biomarkers
Behavioral and activity biomarkers are vital for understanding a patient’s lifestyle and habits, which influence their well-being. The biomarkers offer insights into the patient’s physical activity, their sleep pattern, diet, and nutrition that can be seamlessly monitored via devices.
A fitness band or tracker that can monitor the steps, heartbeat count, calories burned, and more offers real-time data and long-term trends that help users manage their activity levels.
Salient Objectives Biomarkers Help Achieve in RPM
Biomarkers play a primary role in helping achieve the objectives of RPM and ensure seamless healthcare delivery. Here are the key objectives.
1. Early Warning Sign Detection
With biomarkers, healthcare organizations can detect early changes in physiological processes or the progression of diseases. Monitoring the level of biomarkers allows healthcare providers to identify deviations from the normal readings and timely intervention while taking preventive measures. The early detection of symptoms by physicians facilitates quick treatment, reduces hospitalizations, and saves costs and patient outcomes while reducing the disease burden.
For example, in diabetes or any other chronic disease management, monitoring biomarkers such as blood glucose levels remotely can help in the early detection of fluctuations. If a patient’s blood glucose levels consistently show patterns of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, providers can adjust medication dosage or provide dietary recommendations to prevent complications.
2. Customized Treatments
With biomarkers, physicians can obtain valuable insights into individual health status, and they can respond to medical interventions accordingly. Biomarker data allow healthcare providers to customize treatment plans to individual needs and characteristics. Personalized treatment helps with enhanced treatment efficiency, reduces adverse effects, and makes the patient more satisfied.
For example, CYP2C19 genotypic biomarker testing provides valuable insights into individual responses to clopidogrel therapy, a commonly prescribed antiplatelet drug used in cardiovascular disease management. Its impact on treatment outcomes is limited when considered in isolation.
3. Disease Control and Prevention
Biomarkers offer valuable insights into the biological processes that are associated with chronic conditions. Continuous monitoring of the level of biomarker allows providers to track the disease activity and vitals. Biomarkers can help identify patients at increased risk of disease progression or complications.
For example, in cardiovascular disease management, biomarkers such as high-sensitivity cardiac troponin levels can indicate myocardial injury or risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
By facilitating early detection, personalized treatment, and proactive management of chronic conditions, biomarkers contribute to better long-term outcomes for patients.
4. Identifying High-Risk Patients
Biomarkers help identify patients who are at a higher risk of experiencing adverse outcomes or disease progression. They provide valuable information about a patient’s prognosis and likelihood of experiencing specific health outcomes.
For example, as per a report from National Library of Medicine, there is a critical role of biomarkers in enhancing cardiovascular risk assessment and prognosis, with implications for guiding clinical decision-making and improving patient outcomes in the context of CVD (cardiovascular diseases). By utilizing various biomarkers representing various aspects of CVD pathology, healthcare professionals can better stratify patient risk and prognosis, leading to more informed clinical decisions and improved patient outcomes.
5. Research and Development
Biomarkers are key in medical research and making new drugs. They help find out how diseases work and how treatments affect them. Researchers use biomarkers to learn more about diseases and find new ways to treat them. Discovering and confirming biomarkers helps create better tests, predict how diseases will progress, and make treatments that target specific aspects of a disease. This improves how patients are cared for and how well they do.
Epilogue
Integrating biomarkers in RPM is one of the most advanced shifts in healthcare that offers more personalized and proactive patient care. Navigating chronic disease complications in healthcare has become easier with the integration of biomarkers as it allows healthcare providers to detect early symptoms, offer tailored treatment, and prevent diseases.
As healthcare continues to advance, biomarkers have a much brighter future that will offer more opportunities to improve patient care and refine treatment plans. The classification of biomarkers allows for a more comprehensive approach to monitoring patient health, facilitating early detection of health issues, personalized treatment plans, and proactive management of chronic conditions. In this journey towards optimizing healthcare delivery, the role of biomarkers in remote patient monitoring will undoubtedly remain pivotal.
Do share your thoughts in the comment section below!